‘A great many people think they are thinking when they are merely rearranging their prejudices.’ –William James

Two leading neuroscientists, Christof Koch and Susan Greenfield, disagree about the activity that takes place in the brain during subjective experience.
How brain processes translate to consciousness is one of the greatest un-solved questions in science. Although the scientific method can delineate events immediately after the big bang and uncover the biochemical nuts and bolts of the brain, it has utterly failed to satisfactorily explain how subjective experience is created.
As neuroscientists, both of us have made it our life’s goal to try to solve this puzzle. We share many common views, including the important acknowledgment that there is not a single problem of consciousness. Rather, numerous phenomena must be explained—in particular, self-consciousness (the ability to examine one’s own desires and thoughts), the content of consciousness (what you are actually conscious of at any moment), and how brain processes relate to consciousness and to nonconsciousness.
{ Scientific American | Continue reading | PDF | More: Our intuitions about consciousness in other beings and objects reveal a lot about how we think }
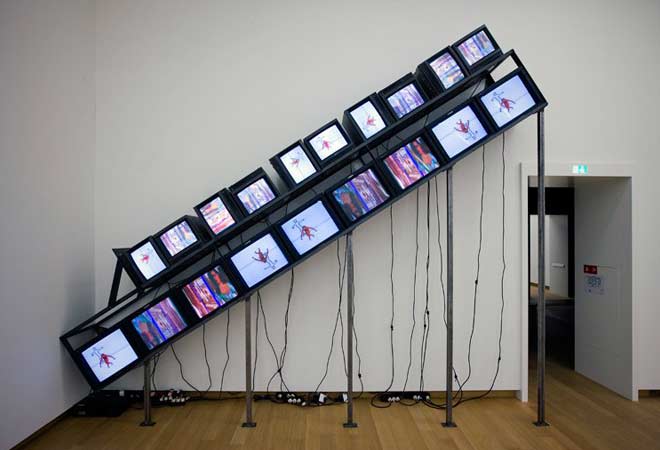
mixed media { Douglas Gordon, Straight to Hell, 2011 }