psychology

Curiosity - the drive for information - is often perceived as a dangerous trait. This is exacerbated by the perception that when something is forbidden, curiosity towards it increases. […]
This research demonstrated the so-called “forbidden fruit effect”, in which unavailable options elicit curiosity – the desire to know more – even when people were completely aware that the forbidden option did not differ from other options in terms of expected outcome, uncertainty (hidden values), and visual salience.
{ OSF | Continue reading }
psychology | February 20th, 2020 8:50 pm
Even though it may come naturally, griping isn’t necessarily always a good thing. Ruminating on negative feelings, and reinforcing them through constant discussion with other people, can lead to catastrophizing, which “is something that can contribute to depression” […]
This can happen because “the more you do something, the more entrenched that path becomes in your brain and the more you continue to do it” […]
Constantly complaining can be an easy way to frustrate our confidantes, but there is research that shows it can also be a useful tool in bonding and helping us process emotions like stress and frustration.
“In short: Yes, it’s good to complain, yes, it’s bad to complain, and yes, there’s a right way to do it” […] The trick to doing it right starts with understanding how the word “complaining” is often misused to describe a variety of behaviors, with some being more harmful or helpful than others. […] there are roughly three categories: venting, problem solving and ruminating, otherwise known as dwelling. […]
Life isn’t perfect. That’s why expressing negative feelings is not only normal, but also healthy, Dr. Kowalski said, adding that the unrealistic expectation that we should always be happy can make us feel worse. […] Inhibiting the disclosure of our dissatisfaction “can produce a negative effect,” she said, because it not only stops us from naming our problem but also prevents us from getting to the root of it.
That’s why “complaining is, ideally, totally solutions focused,” Ms. Gilbertson said. Though venting is not as focused on solving problems, “there are also really positive benefits,” Dr. Grice said, because it allows us “to get things out in the open and get our feelings heard so they don’t build up and cause stress.” […]
You want to avoid what Dr. Grice calls wearing “muddy glasses,” where no matter what’s going on you always find something to complain about. The same goes with rehashing a problem over and over again, whether with friends or in the echo chamber of the internet.
{ NY Times | Continue reading }
psychology | January 27th, 2020 9:14 pm
The latest research, published on Friday by two psychology professors, combs through about 40 studies that have examined the link between social media use and both depression and anxiety among adolescents. That link, according to the professors, is small and inconsistent. […]
In most cases, [most researchers] say, the phone is just a mirror that reveals the problems a child would have even without the phone. […]
“The current dominant discourse around phones and well-being is a lot of hype and a lot of fear,” Mr. Hancock said. “But if you compare the effects of your phone to eating properly or sleeping or smoking, it’s not even close.”
Mr. Hancock’s analysis of about 226 studies on the well-being of phone users concluded that “when you look at all these different kinds of well-being, the net effect size is essentially zero.”
{ NY Times | Continue reading }
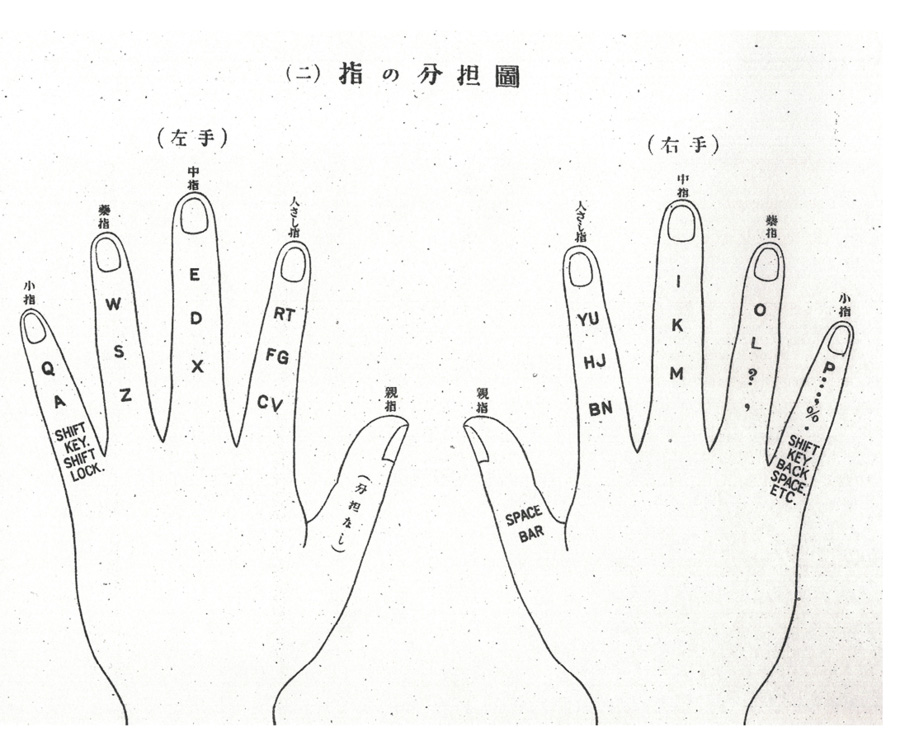
image { Diagram from a 1923 Japanese typewriting manual }
psychology, social networks | January 23rd, 2020 6:53 pm

He had diabetes, and he had signed up for a study to see if taking a “statin” – a kind of cholesterol-lowering drug – might help. So far, so normal.
But soon after he began the treatment, his wife began to notice a sinister transformation. A previously reasonable man, he became explosively angry and – out of nowhere – developed a tendency for road rage. During one memorable episode, he warned his family to keep away, lest he put them in hospital. […]
In 2018, a study uncovered the same effect in fish. Giving statins to Nile tilapia made them more confrontational and – crucially – altered the levels of serotonin in their brains. This suggests that the mechanism that links cholesterol and violence may have been around for millions of years.
Golomb remains convinced that lower cholesterol, and, by extension, statins, can cause behavioural changes in both men and women, though the strength of the effect varies drastically from person to person. […]
The world is in the midst of a crisis of over-medication, with the US alone buying up 49,000 tonnes of paracetamol every year – equivalent to about 298 paracetamol tablets per person. [..]
Mischkowski’s own research has uncovered a sinister side-effect of paracetamol. For a long time, scientists have known that the drug blunts physical pain by reducing activity in certain brain areas, such as the insular cortex, which plays an important role in our emotions. These areas are involved in our experience of social pain, too – and intriguingly, paracetamol can make us feel better after a rejection.
And recent research has revealed that this patch of cerebral real-estate is more crowded than anyone previously thought, because it turns out the brain’s pain centres also share their home with empathy. […] results revealed that paracetamol significantly reduces our ability to feel positive empathy – a result with implications for how the drug is shaping the social relationships of millions of people every day. […] Technically, paracetamol isn’t changing our personalities, because the effects only last a few hours and few of us take it continuously.
{ BBC | Continue reading }
photo { Logan White }
drugs, health, photogs, psychology | January 12th, 2020 9:02 pm

Using Music as Medicine – finding the optimum music listening ‘dosage’
There was a general agreement of dosage time across 3 of the 4 domains with 11 minutes being the most common amount of time it took for people to receive the therapeutic benefit from their self- selected music preferences. The only exception was the domain of happiness where the most common length of time for people to become happier after listening to their chosen music was reduced to 5 minutes, suggesting that happy music takes less time to take effect than other music.
{ British Academy of Sound Therapy.com | PDF | More
photo { Sarah Illenberger }
eudaemonism, music, psychology | January 12th, 2020 5:07 pm

Most of the research on happiness has documented that income, marriage, employment and health affect happiness. Very few studies examine whether happiness itself affect income, marriage, employment and health. […] Findings show that happier Indonesians in 2007 earned more money, were more likely to be married, were less likely to be divorced or unemployed, and were in better health when the survey was conducted again seven years later.
{ Applied Research in Quality of Life | Continue reading }
image { Maurizio Cattelan and Pierpaolo Ferrari, Toilet Paper #1, June 2010 }
eudaemonism, psychology | November 30th, 2019 1:24 pm

Across four studies participants (N = 818) rated the profoundness of abstract art images accompanied with varying categories of titles, including: pseudo-profound bullshit titles (e.g., The Deaf Echo), mundane titles (e.g., Canvas 8), and no titles.
Randomly generated pseudo-profound bullshit titles increased the perceived profoundness of computer-generated abstract art, compared to when no titles were present (Study 1).
Mundane titles did not enhance the perception of profoundness, indicating that pseudo-profound bullshit titles specifically (as opposed to titles in general) enhance the perceived profoundness of abstract art (Study 2).
Furthermore, these effects generalize to artist-created abstract art (Study 3).
Finally, we report a large correlation between profoundness ratings for pseudo-profound bullshit and “International Art English” statements (Study 4), a mode and style of communication commonly employed by artists to discuss their work.
{ Judgment and Decision Making | Continue reading }
art, buffoons, psychology | November 30th, 2019 1:24 pm

According to a paper published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, you can come off as more persuasive by speaking slightly louder than you normally do, and by varying the overall volume of your voice (i.e., speaking both more loudly and softly). […] it will make you appear more confident when you speak, which has a positive impact on your overall persuasiveness, according to the study.
{ NY Times | Continue reading }
noise and signals, psychology, relationships | November 14th, 2019 8:00 am

“The human eye is extraordinarily sensitive to light,” Dr. Woods said. Throw a few dozen photons its way, a few dozen quantum-sized packets of light, and the eye can readily track them. […]
N.I.S.T. disk number two was an example of advanced ultra-black technology: elaborately engineered arrays of tiny carbon cylinders, or nanotubes, designed to capture and muzzle any light they encounter. […] The N.I.S.T. ultra-black absorbs at least 99.99 percent of the light that stumbles into its nanotube forest. But scientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology reported in September the creation of a carbon nanotube coating that they claim captures better than 99.995 of the incident light. “The blackest black should be a constantly improving number,” said Brian Wardle, a professor of aeronautics and astronautics and an author on the new report. “Folks will find other materials that are blacker than ours.” […]
Psychologists have gathered evidence that black is among the most metaphorically loaded of all colors, and that we absorb our often contradictory impressions about black at a young age. […] Participants were asked to link images with traits. Which boy was likeliest to cheat on the test? Which man was likely to be in charge at work? Which girl was the smartest in her class, which dog the scariest? Again and again, among both children and young adults, black pulled ahead of nearly every color but red. Black was the color of cheating, and black was the color of cleverness. A black tie was the mark of a boss, a black collar the sign of a pit bull. Black was the color of strength and of winning. Black was the color of rage. […]
Diemut Strebe, an artist in residence at M.I.T., collaborated with Dr. Wardle on a project that would merge carbon at its most absorptive configuration, in the form of carbon nanotubes, with carbon in its most reflective and refractive state, as a diamond. One of their biggest challenges: finding a jeweler willing to lend them a chunky diamond that would be plastered with what amounts to high-tech soot. “I tried many companies, Tiffany, others,” Ms. Strebe said. “I got many no’s.” Finally, L.J. West Diamonds, which specializes in colored diamonds, agreed to hand over a $2 million, 16.78-carat yellow diamond, provided the process could be reverse-engineered and the carbon nanotube coating safely removed. The resulting blackened bling is on view at the New York Stock Exchange, which Ms. Strebe calls “the holy grail of valuation.”
{ NY Times | Continue reading }
colors, psychology, science, technology | November 11th, 2019 8:09 pm

Do a country’s inhabitants get happier as it gets richer? […]
In Britain, for example, happiness fell sharply during the two world wars. It began to rise again after 1945, peaked in 1950, and then fell gradually, including through the so-called Swinging Sixties, until it reached a nadir around 1980.
America’s national happiness, too, fell during the world wars. It also fell in the 1860s, during and after the country’s civil war. The lowest point of all came in 1975, at the end of a long decline during the Vietnam war, with the fall of Saigon and America’s humiliating defeat.
In Germany and Italy the first world war also caused dips in happiness. By contrast, during the second world war these countries both got happier as the war continued. […]
A one-year increase in longevity has the same effect on national happiness as a 4.3% increase in gdp. […]
it is warfare that causes the biggest drops in happiness. On average it takes a 30% increase in gdp to raise happiness by the amount that a year of war causes it to fall. The upshot appears to be that, while increasing national income is important to happiness, it is not as important as ensuring the population is healthy and avoiding conflict.
{ The Economist | Continue reading }
economics, fights, health, psychology | October 20th, 2019 2:43 pm

Stendhal syndrome, Stendhal’s syndrome or Florence syndrome is a psychosomatic condition involving rapid heartbeat, fainting, confusion and even hallucinations, allegedly occurring when individuals become exposed to objects or phenomena of great beauty.
Although psychologists have long debated whether Stendhal’s syndrome exists, the apparent effects on some individuals are severe enough to warrant medical attention.
Though there are numerous accounts of people fainting while taking in Florentine art, dating from the early 19th century on, the syndrome was only named in 1979; when it was described by Italian psychiatrist Graziella Magherini, who observed over a hundred similar cases among tourists in Florence.
{ Wikipedia | Continue reading }
beaux-arts, psychology | October 10th, 2019 12:51 pm
psychology, sleep | October 6th, 2019 10:48 am

A standard response of both policy makers and private citizens to hardships—from natural disasters to mass shootings—is to offer “thoughts and prayers.” Critics argue that such gestures are meaningless and may obstruct structural reforms intended to mitigate catastrophes. In this study, we elicit the value of receiving thoughts and prayers from strangers following adversity. We find that Christians value thoughts and prayers from religious strangers and priests, while atheists and agnostics are “prayer averse”—willing to pay to avoid receiving prayers. Furthermore, while indifferent to receiving thoughts from other secular people, they negatively value thoughts from Christians.
{ PNAS | Continue reading }
photo { Guy Bourdin | Vogue France, May 1970 }
psychology | September 30th, 2019 6:25 pm

studies have shown that America has been getting more narcissistic since the Seventies […] one study found narcissistic traits to be rising as quickly as obesity, while yet another showed that almost one-third of high school students in America in 2005 said that they expected to eventually become famous.
{ Rolling Stone | Continue reading }
U.S., psychology | September 2nd, 2019 3:53 am

When faced with a personal problem people typically give better advice to others than to themselves. This has been termed ‘Solomon’s Paradox’, named after the biblical King Solomon who was wise for others, but not so when it came to making decisions that would have an impact on his own standing.
Suppose that instead of imagining a problem from the perspective of another you were actually able to have a conversation with yourself about it, but from the embodied perspective of another.
A previous study showed how it is possible to enact internal dialogue in virtual reality (VR) through participants alternately occupying two different virtual bodies – one representing themselves and the other Sigmund Freud. They could maintain a self-conversation by explaining their problem to the virtual Freud and then from the embodied perspective of Freud see and hear the explanation by their virtual doppelganger, and then give some advice. Alternating between the two bodies they could maintain a self-dialogue, as if between two different people.
Here we show that the process of alternating between their own and the Freud body is important for successful psychological outcomes. An experiment was carried out with 58 people, 29 in the body swapping Self-Conversation condition and 29 in a condition where they only spoke to a Scripted Freud character. The results showed that the Self-Conversation method results in a greater perception of change and help compared to the Scripted. We compare this method with the distancing paradigm where participants imagine resolving a problem from a first or third person perspective.
We consider the method as a possible strategy for self-counselling.
{ Nature | Continue reading }
synthetic polymer and silkscreen ink on canvas { Andy Warhol, Are You “Different?” (Positive), 1985 }
psychology, warhol | August 4th, 2019 1:10 pm
We analyzed over one million posts from over 4,000 individuals on several social media platforms, using computational models based on reward reinforcement learning theory. Our results consistently show that human behavior on social media qualitatively and quantitatively conforms to the principles of reward learning.
{ PsyArXiv | Continue reading }
image { Dissecting Reinforcement Learning }
psychology, social networks | July 15th, 2019 1:21 pm
Suppose you live in a deeply divided society: 60% of people strongly identify with Group A, and the other 40% strongly identify with Group B. While you plainly belong to Group A, you’re convinced this division is bad: It would be much better if everyone felt like they belonged to Group AB. You seek a cohesive society, where everyone feels like they’re on the same team.
What’s the best way to bring this cohesion about? Your all-too-human impulse is to loudly preach the value of cohesion. But on reflection, this is probably counter-productive. When members of Group B hear you, they’re going to take “cohesion” as a euphemism for “abandon your identity, and submit to the dominance of Group A. ”None too enticing. And when members of Group A notice Group B’s recalcitrance, they’re probably going to think, “We offer Group B the olive branch of cohesion, and they spit in our faces. Typical.” Instead of forging As and Bs into one people, preaching cohesion tears them further apart.
What’s the alternative? Simple. Instead of preaching cohesion, reach out to Group B. Unilaterally show them respect.Unilaterally show them friendliness. They’ll be distrustful at first, but cohesion can’t be built in a day.
{ The Library of Economics and Liberty | Continue reading }
photo { Stephen Shore, Queens, New York, April 1972 }
ideas, photogs, psychology, relationships | June 16th, 2019 2:01 pm

There’s been an explosion of interest in the use of psychedelics in psychiatry. […]
Psychedelics have mostly been investigated in small studies run by true believers. […] Some of the most exciting psychedelic findings have already failed to replicate […]
Ketamine is the best comparison for psychedelics. […] Like psychedelics, it got hyped as an exciting new innovation that was going to revolutionize everything in psychiatry (in this case, depression treatment). But it’s been in pretty common (albeit non-formulary) use for five years now, and nothing has been revolutionized. […]
Between 10% and 50% of Americans have tried psychedelics. If psychedelics did something shocking, we would already know about it. […]
Even if all of the above are wrong and psychedelics work very well, the FDA could kill them with a thousand paper cuts. Again, look at ketamine: the new FDA approval ensures people will be getting the slightly different esketamine, through a weird route of administration, while paying $600 a pop, in specialized clinics that will probably be hard to find. Given the price and inconvenience, insurance companies will probably restrict it to the most treatment-resistant patients, and it probably won’t help them (treatment-resistant patients tend to stay that way). Given the panic around psychedelics, I expect it to be similarly difficult to get them even if they are legal and technically FDA-approved. Depressed people will never be able to walk into a psychiatrist’s office and get LSD. They’ll walk into a psychiatrist’s office, try Prozac for three months, try Wellbutrin for three months, argue with their insurance for a while, eventually get permission to drive to a city an hour away that has a government-licensed LSD clinic, and get some weird form of LSD that might or might not work, using a procedure optimized to minimize hallucinations.
{ Slate Star Codex | Continue reading }
drugs, health, psychology | May 13th, 2019 10:19 am

Physical pain represents a common feature of Bondage and Discipline/Dominance and Submission/Sadism and Machochism (BDSM) activity. This article explores the literature accounting for how painful stimuli may be experienced as pleasurable among practitioners of BDSM, and contrasting this with how it is experienced as painful among non-BDSM individuals. […] The experience of pain in this context can bring about altered states of consciousness that may be similar to what occurs during mindfulness meditation.
{ The Journal of Sex Research | Continue reading }
fetish, neurosciences, psychology | May 9th, 2019 1:11 pm

According to the 2019 World Happiness Report, negative feelings are rising around the world—and the United States is particularly hard hit with an “epidemic of addictions.” Tellingly, the report also shows a widening happiness gap, with some people reporting much more well-being and others showing much less within each country. […]
Negative feelings—worry, sadness, and anger—have been rising around the world, up by 27 percent from 2010 to 2018. […]
“The U.S. is suffering an epidemic of addictions.” This includes an addiction to technology, which researcher Jean Twenge largely blames for the worrying mental health trends among U.S. adolescents. In her chapter of the report, she argues that screen time is displacing activities that are key to our happiness, like in-person social contact. Forty-five percent of adolescents are online “almost constantly,” and the average high school senior spends six hours a day texting, on social media or on the internet.
But we’re hooked on more than just technology. According to researcher Steve Sussman, around half of Americans suffer from at least one addiction. Some of the most prevalent are alcohol, food, and work—which each affect around 10 percent of adults—as well as drugs, gambling, exercise, shopping, and sex.
There’s another possible explanation for unhappiness, though: Governments are losing their way. […] According to survey results since 2005, people across the globe are more satisfied with life when their governments are more effective, enforce the rule of law, have better regulation, control corruption, and spend in certain ways—more on health care and less on military.
{ Yes | Continue reading }
eudaemonism, psychology | May 1st, 2019 10:54 am