photogs

ExxonMobil, Shell, and Saudi Aramco are ramping up output of plastic—which is made from oil and gas, and their byproducts—to hedge against the possibility that a serious global response to climate change might reduce demand for their fuels, analysts say. Petrochemicals, the category that includes plastic, now account for 14 percent of oil use and are expected to drive half of oil demand growth between now and 2050, the International Energy Agency (IEA) says. The World Economic Forum predicts plastic production will double in the next 20 years.
{ Wired | Continue reading | Thanks Tim }
previously { The missing 99%: why can’t we find the vast majority of ocean plastic? }
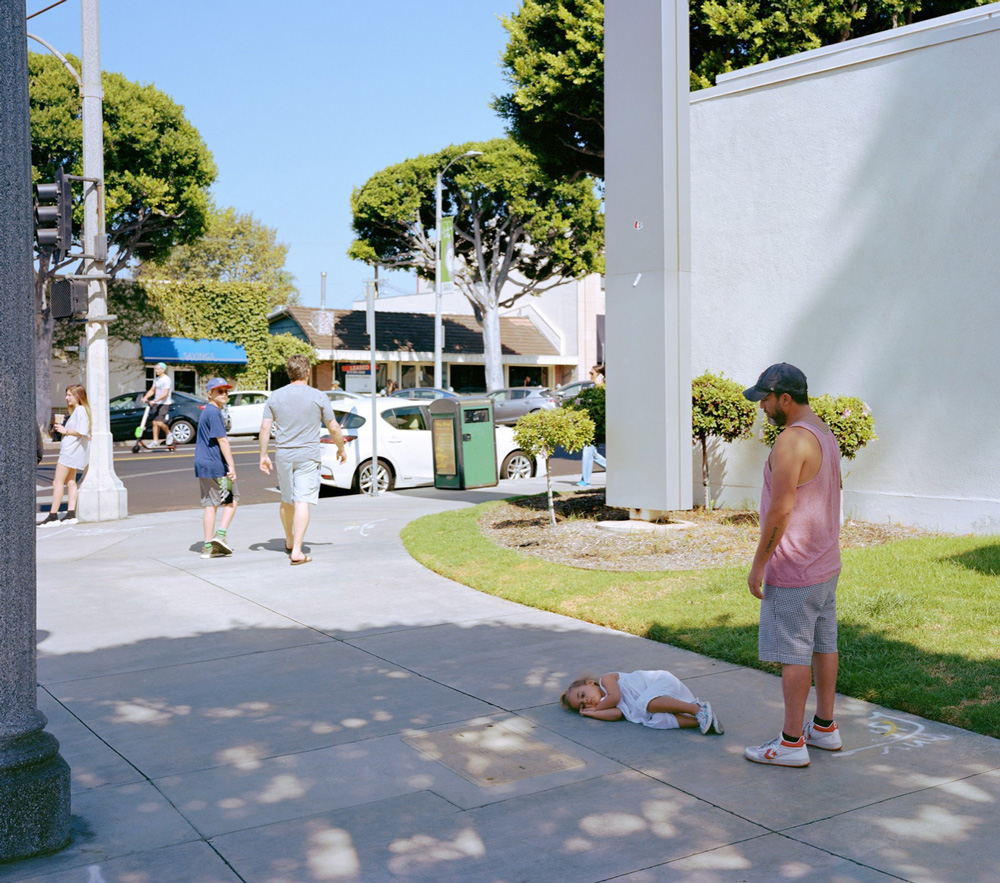
photo { Kate Ballis }
economics, gross, oil, photogs | January 22nd, 2020 4:49 pm

He had diabetes, and he had signed up for a study to see if taking a “statin” – a kind of cholesterol-lowering drug – might help. So far, so normal.
But soon after he began the treatment, his wife began to notice a sinister transformation. A previously reasonable man, he became explosively angry and – out of nowhere – developed a tendency for road rage. During one memorable episode, he warned his family to keep away, lest he put them in hospital. […]
In 2018, a study uncovered the same effect in fish. Giving statins to Nile tilapia made them more confrontational and – crucially – altered the levels of serotonin in their brains. This suggests that the mechanism that links cholesterol and violence may have been around for millions of years.
Golomb remains convinced that lower cholesterol, and, by extension, statins, can cause behavioural changes in both men and women, though the strength of the effect varies drastically from person to person. […]
The world is in the midst of a crisis of over-medication, with the US alone buying up 49,000 tonnes of paracetamol every year – equivalent to about 298 paracetamol tablets per person. [..]
Mischkowski’s own research has uncovered a sinister side-effect of paracetamol. For a long time, scientists have known that the drug blunts physical pain by reducing activity in certain brain areas, such as the insular cortex, which plays an important role in our emotions. These areas are involved in our experience of social pain, too – and intriguingly, paracetamol can make us feel better after a rejection.
And recent research has revealed that this patch of cerebral real-estate is more crowded than anyone previously thought, because it turns out the brain’s pain centres also share their home with empathy. […] results revealed that paracetamol significantly reduces our ability to feel positive empathy – a result with implications for how the drug is shaping the social relationships of millions of people every day. […] Technically, paracetamol isn’t changing our personalities, because the effects only last a few hours and few of us take it continuously.
{ BBC | Continue reading }
photo { Logan White }
drugs, health, photogs, psychology | January 12th, 2020 9:02 pm

“Financial machine learning creates a number of challenges for the 6.14 million people employed in the finance and insurance industry, many of whom will lose their jobs — not necessarily because they are replaced by machines, but because they are not trained to work alongside algorithms,” said Marcos Lopez de Prado, a Cornell University professor. […]
Nasdaq runs more than 40 different algorithms, using about 35,000 parameters, to look for market abuse and manipulation in real time.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
related { 90% of high-tech job growth concentrated in just 5 cities: Boston, San Francisco, San Jose, Seattle and San Diego }
photo { Matthew Reamer }
economics, photogs, robots & ai, traders | December 10th, 2019 9:42 am

Urgency Reader is a quick assembling of texts, risograph printed in Pawtucket, RI, and bound as a book at the last minute to launch at the Odds and Ends Art Book Fair at Yale University Art Gallery on December 6, 2019. […] Inspired by Omnibus News #1 (1969), Assembling (1970–87), and other assembling publications, Urgency Reader is an experiment in publishing as a gesture of call and response: the quick circulation of a charged collection of texts—in some cases raw, in-progress, or sketchy—to a small but deeply engaged audience. […] The order of the texts as they appear in the book was determined by chance by assigning a series of random integers from random.org to the alphabetical list of contributors.
{ Paul Soulellis | Continue reading + Download }
In 1969 three Germans, Thomas Niggl, Christian D’Orville and Heimrad Prem, issued a call for submissions for a periodical in which interested individuals were invited to submit up to 2 pages of art works in an edition of 1500 copies each. Contributors were responsible for the cost of reproducing their own submissions, and all works would be accepted with no editing or censorship. Published the same year under the title Omnibus News, the periodical was comprised of 192 submissions (384 pages) sequenced alphabetically in an A4 format and in an edition of 1500.
{ Arte Contemporanea | Continue reading }
photos { Tania Franco Klein | Adrià Cañameras }
fire, photogs, press | December 8th, 2019 8:19 am
animals, photogs | November 2nd, 2019 8:47 pm
Suppose you live in a deeply divided society: 60% of people strongly identify with Group A, and the other 40% strongly identify with Group B. While you plainly belong to Group A, you’re convinced this division is bad: It would be much better if everyone felt like they belonged to Group AB. You seek a cohesive society, where everyone feels like they’re on the same team.
What’s the best way to bring this cohesion about? Your all-too-human impulse is to loudly preach the value of cohesion. But on reflection, this is probably counter-productive. When members of Group B hear you, they’re going to take “cohesion” as a euphemism for “abandon your identity, and submit to the dominance of Group A. ”None too enticing. And when members of Group A notice Group B’s recalcitrance, they’re probably going to think, “We offer Group B the olive branch of cohesion, and they spit in our faces. Typical.” Instead of forging As and Bs into one people, preaching cohesion tears them further apart.
What’s the alternative? Simple. Instead of preaching cohesion, reach out to Group B. Unilaterally show them respect.Unilaterally show them friendliness. They’ll be distrustful at first, but cohesion can’t be built in a day.
{ The Library of Economics and Liberty | Continue reading }
photo { Stephen Shore, Queens, New York, April 1972 }
ideas, photogs, psychology, relationships | June 16th, 2019 2:01 pm

Can events be accurately described as historic at the time they are happening?
Claims of this sort are in effect predictions about the evaluations of future historians; that is, that they will regard the events in question as significant.
Here we provide empirical evidence in support of earlier philosophical arguments1 that such claims are likely to be spurious and that, conversely, many events that will one day be viewed as historic attract little attention at the time.
{ Nature Human Behaviour | Continue reading }
photo { David Sims }
ideas, photogs | June 13th, 2019 12:33 pm

Weather forecasters need a ton of knowledge and a fair bit of experience with local weather patterns to do their job well. They also need a good forecast model. These computer models take in measurements from weather stations on the ground, satellites in orbit, and balloons in between and then simulate the physics of weather forward in time a few days.
For the first time in about 40 years, the guts of the US model got swapped out for something new today. The upgrade brings us a new “Finite-Volume Cubed-Sphere” (or FV3) dynamical core, which simulates the basic atmospheric physics at the heart of this endeavor, a change that has been in the works for a while.
{ ArsTechnica | Continue reading }
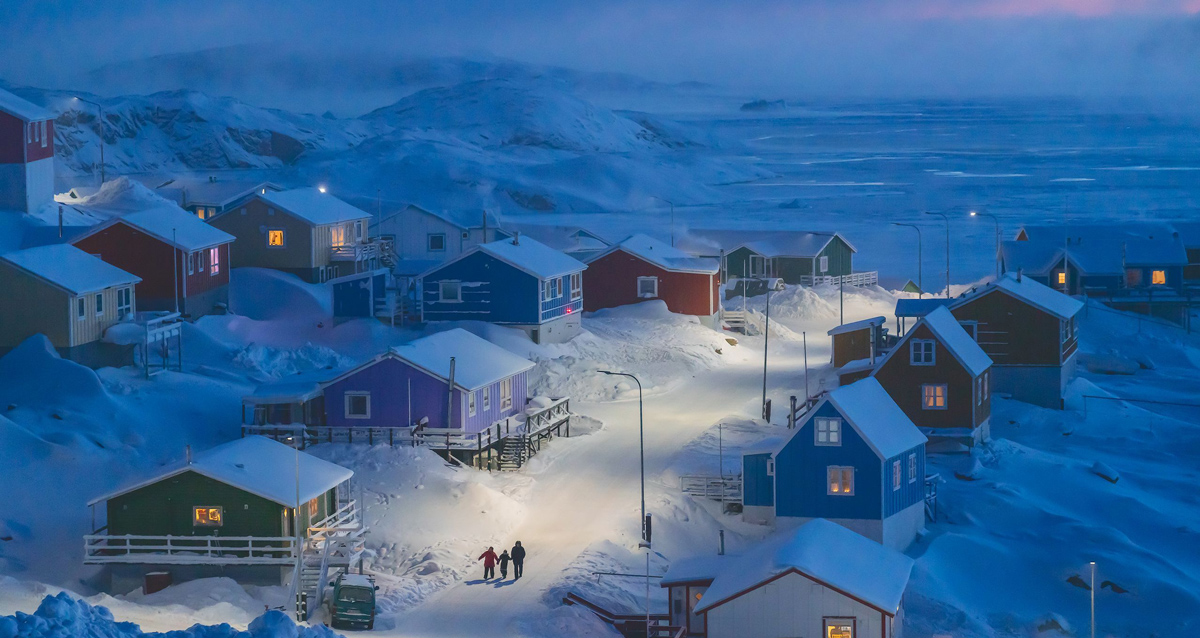
photo { The main prize in the 2019 National Geographic Travel Photographer of the Year Contest went to Chu Weimin | Upernavik is a fishing village on a tiny island in west Greenland. Historically, Greenlandic buildings were painted different colors to indicate different functions, from red storefronts to blue fishermen’s homes—a useful distinction when the landscape is blanketed in snow. }
photogs, within the world | June 13th, 2019 11:29 am

If you wear designer glasses, there’s a very good chance you’re wearing Luxottica frames.
The company’s owned and licensed brands include Armani, Brooks Brothers, Burberry, Chanel, Coach, DKNY, Dolce & Gabbana, Michael Kors, Oakley, Oliver Peoples, Persol, Polo Ralph Lauren, Ray-Ban, Tiffany, Valentino, Vogue and Versace.
Along with LensCrafters, Luxottica also runs Pearle Vision, Sears Optical, Sunglass Hut and Target Optical, as well as the insurer EyeMed Vision Care.
And Italy’s Luxottica now casts an even longer shadow over the eyewear industry after merging last fall with France’s Essilor, the world’s leading maker of prescription eyeglass lenses and contact lenses. The combined entity is called EssilorLuxottica. […]
“You can get amazingly good frames, with a Warby Parker level of quality, for $4 to $8,” Butler said. “For $15, you can get designer-quality frames, like what you’d get from Prada.”
And lenses? “You can buy absolutely first-quality lenses for $1.25 apiece,” Butler said.
Yet those same frames and lenses might sell in the United States for $800.
{ Los Angeles Times | Continue reading }
photo { Jeff Wall, Parent child, 2018 }
economics, eyes, photogs | May 27th, 2019 7:42 am
photogs | May 21st, 2019 12:49 pm

Products developed by companies such as Activtrak allow employers to track which websites staff visit, how long they spend on sites deemed “unproductive” and set alarms triggered by content considered dangerous. […]
To quantify productivity, “profiles” of employee behaviour — which can be as granular as mapping an individual’s daily activity — are generated from “vast” amounts of data. […]
If combined with personal details, such as someone’s age and sex, the data could allow employers to develop a nuanced picture of ideal employees, choose whom they considered most useful and help with promotion and firing decisions. […]
Some technology, including Teramind’s and Activtrak’s, permits employers to take periodic computer screenshots or screen-videos — either with employees’ knowledge or in “stealth” mode — and use AI to assess what it captures.
Depending on the employer’s settings, screenshot analysis can alert them to things like violent content or time spent on LinkedIn job adverts.
But screenshots could also include the details of private messages, social media activity or credit card details in ecommerce checkouts, which would then all be saved to the employer’s database. […]
Meanwhile, smart assistants, such as Amazon’s Alexa for Business, are being introduced into workplaces, but it is unclear how much of office life the devices might record, or what records employers might be able to access.
{ Financial Times | Continue reading }
Google uses Gmail to track a history of things you buy. […] Google says it doesn’t use this information to sell you ads.
{ CNBC | Continue reading }
unrelated { Navy Seal’s lawyers received emails embedded with tracking software }
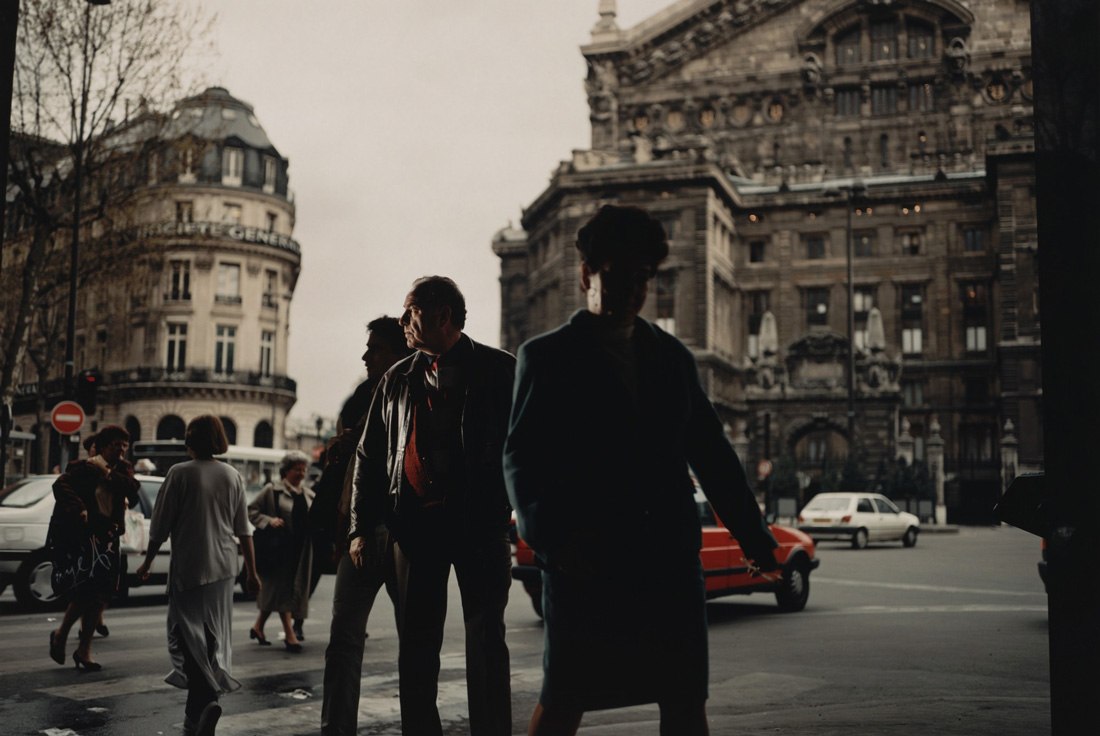
photo { Philip-Lorca diCorcia, Paris, 1996 }
photogs, spy & security, technology | May 21st, 2019 11:36 am

If you know that a public company has done a bad thing, and no one else knows about it, how can you use that knowledge to make money? […]
This is a financial column, so we tend to focus on the financial-markets answers: You can short the company’s stock, or buy put options, or buy credit-default swaps. Then you can either sit back and let the market discover the bad thing, or you can bring it to the market’s attention, by announcing the bad thing and maybe also by taking some extra steps—generally suing or calling up a regulator—to get the ball rolling. This approach has some crucial advantages; most notably, if the company is very big and the thing is very bad, this is a good way to make a whole lot of money. But there are disadvantages too. You tend to need a lot of capital to make a lot of money doing this; if you don’t have enough money to make a big bet against the company, you’ll probably have to sell your idea to a hedge fund that does, and you’ll get only a portion of the upside. There are all the general financial risks of short selling: The stock could go up for reasons unrelated to the bad thing, “the market can remain irrational longer than you can remain solvent,” etc. There are the specific risks of noisy short selling: The company will accuse you of fraud, people won’t believe your revelations because you have money at stake, etc. There is also the risk of insider trading: Depending on how you came to know of the secret bad thing, there may be some legal risk to you from trading on it.
But those are just the markets-y ways to make money from misbehavior. There are also lots of lawyer-y ways. There are whistleblower programs that can reward you for telling regulators—particularly the Securities and Exchange Commission—about the bad thing. (The SEC’s program focuses on securities fraud, of course, but everything is securities fraud so you can be creative.) If you are a lawyer looking to profit from the bad thing, you can find a victim of the bad thing and sue for damages (and take a cut), or you can find holders of the company’s securities and sue for securities fraud (and take a bigger cut), because, again, everything is securities fraud. […]
The really long game, if you are a lawyer, is that you can become a federal prosecutor, investigate the company for misconduct, push it to hire a fancy law firm staffed with former federal prosecutors to conduct an expensive internal investigation, and enter into a non-prosecution agreement that requires the company to pay millions of dollars to an outside monitor who is also a former federal prosecutor. Do a few of these—expanding the scope of criminal liability for corporations, and normalizing the notion that corporations should resolve their criminal liability by hiring ex-prosecutors as monitors and investigators—and then leave for a private law firm where you get paid to do the investigations and the monitoring, while the next generation of prosecutors creates business for you. […]
Avenatti clearly did not do a good enough job of making the extortion look like something else to satisfy prosecutors. I don’t know if he did enough to satisfy a jury; perhaps we’ll find out. But he didn’t do nothing; the complaint contains some gestures in the direction of Avenatti being a legitimate lawyer with a legitimate case from a legitimate client trying to reach a legitimate settlement. He didn’t just ask for money; he demanded that Nike do an internal investigation and that he be in charge of it. (And be paid a lot.) It’s not pure, naked blackmail; it is a settlement negotiation that gets a little deeper into blackmail territory than you’d ideally like. But any settlement negotiation is, you know, “give me money or I will sue and that will be embarrassing for you,” so it is a matter of degrees.
{ Matt Levine/Bloomberg | Continue reading }
pigment ink on cotton paper { Aneta Grzeszykowska, Beauty Mask #10, 2017 }
law, photogs | March 26th, 2019 3:23 pm
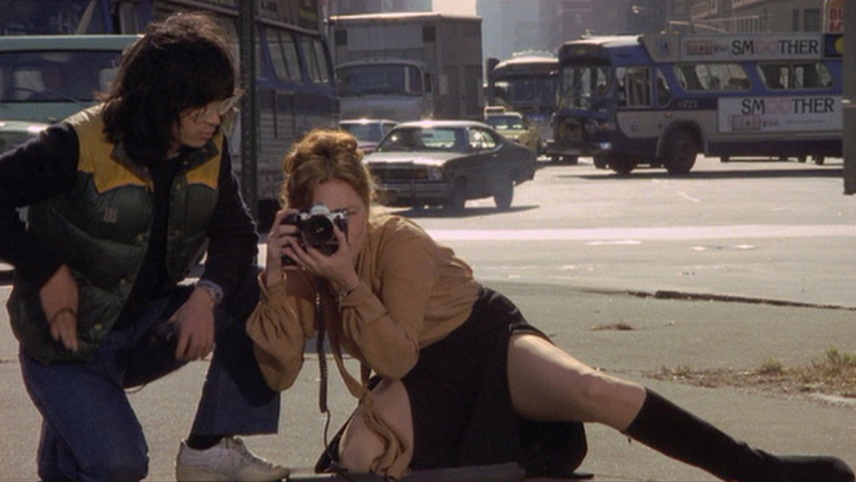

Litigation stemming from an incident in which a middle-aged woman tripped while stepping backward to take a photograph, and without first looking in her direction of travel, led to an observational study of the frequency with which people taking photographs step back without first looking where they were stepping. Prior research on looking before stepping backward did not exist.
Research assistants asked a convenience sample of middle-aged women to take a photograph of the assistants standing in front of a building. The task required the participants to step away from the building. The study found that 87% of the participants looked back at least once before or during a backward step, and that 83% of the steps away from the building were preceded by or accompanied by a look in the direction of travel. Suggestions for future research are provided.
{ Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting }
related { “The First Moonwalk” — Bill Bailey at the Apollo Theatre, New York, 1955 }
unrelated { Man accused of sexually abusing minor identifies himself as Michael Jackson }
still image { Faye Dunaway in Eyes of Laura Mars, 1978 }
photogs, science | March 26th, 2019 3:03 pm
photogs | January 21st, 2019 8:53 am

The vast majority of life on Earth depends, either directly or indirectly, on photosynthesis for its energy. And photosynthesis depends on an enzyme called RuBisCO, which uses carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to build sugars. So, by extension, RuBisCO may be the most important catalyst on the planet.
Unfortunately, RuBisCO is, well, terrible at its job. It might not be obvious based on the plant growth around us, but the enzyme is not especially efficient at catalyzing the carbon dioxide reaction. And, worse still, it often uses oxygen instead. This produces a useless byproduct that, if allowed to build up, will eventually shut down photosynthesis entirely. It’s estimated that crops such as wheat and rice lose anywhere from 20 to 50 percent of their growth potential due to this byproduct.
While plants have evolved ways of dealing with this byproduct, they’re not especially efficient. So a group of researchers at the University of Illinois, Urbana decided to step in and engineer a better way. The result? In field tests, the engineered plants grew up to 40 percent more mass than ones that relied on the normal pathways.
{ Ars Technica | Continue reading }
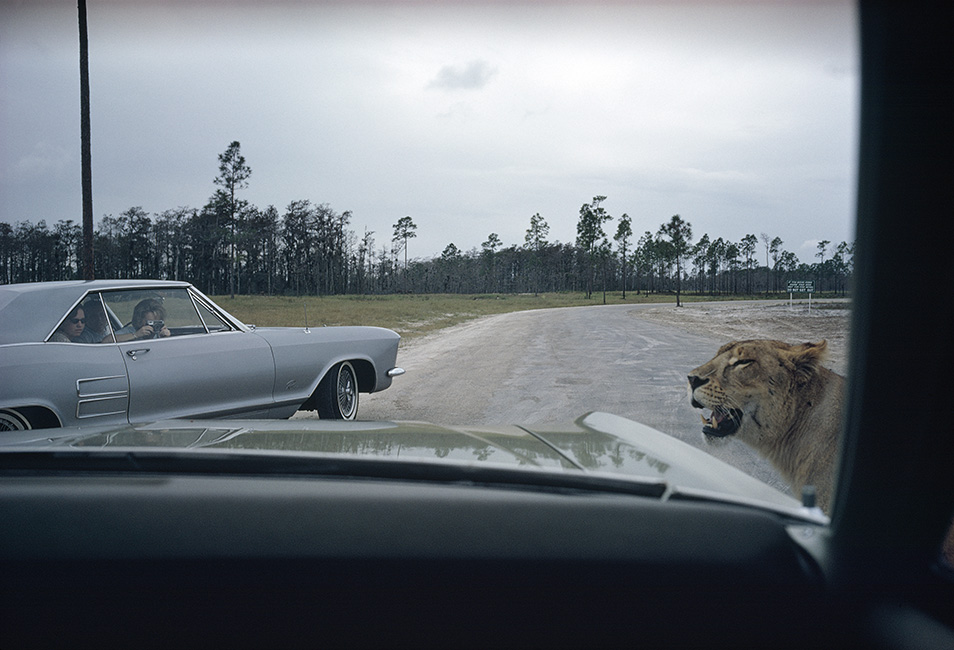
photo { Joel Meyerowitz, Florida, 1970 }
Botany, chem, photogs, science | January 11th, 2019 8:22 am
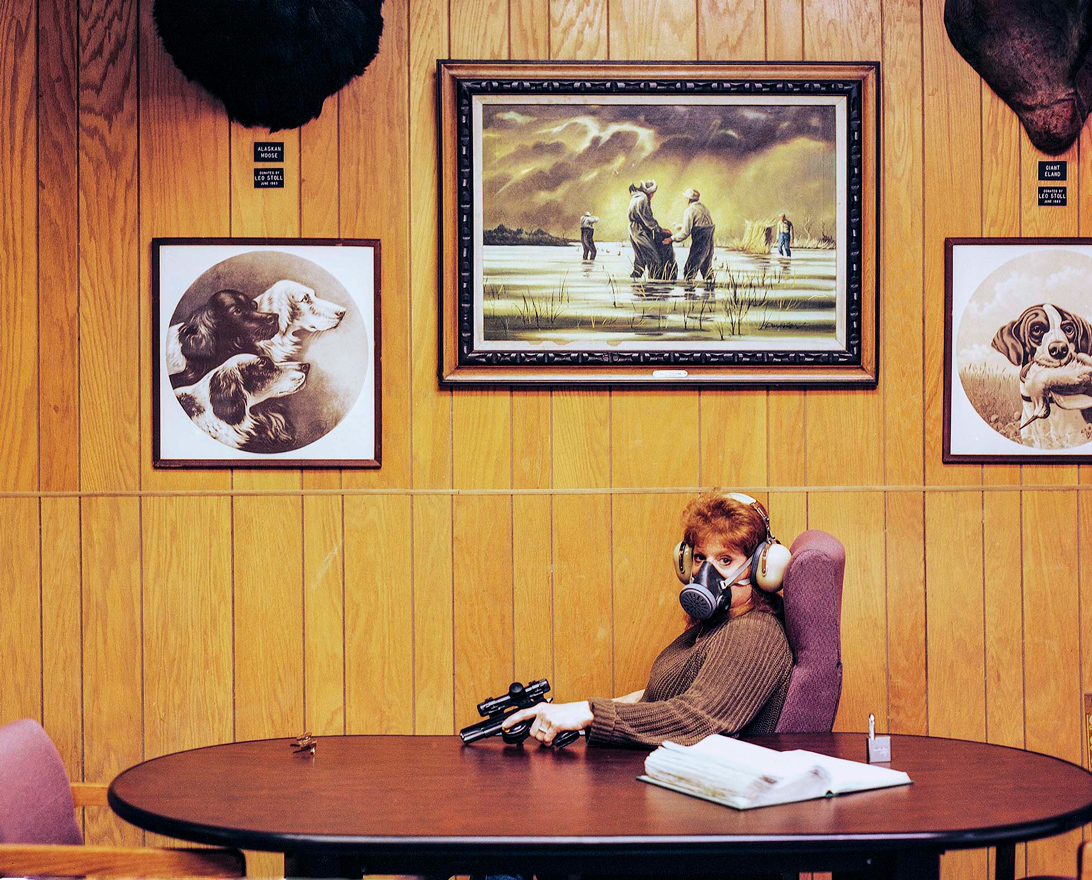

According to the most comprehensive survey of casualties (both fatal and nonfatal), 21 percent of the casualties in World War II were attributable to friendly fire, 39 percent of the casualties in Vietnam, and 52 percent of the casualties in the first Gulf War.
{ Wikipedia | Continue reading }
photo { Jason Florio | The Metropolitan Rod and Gun Club, established in 1936, is New York’s longest running sporting firearms club }
fights, guns, photogs | November 8th, 2018 1:25 pm
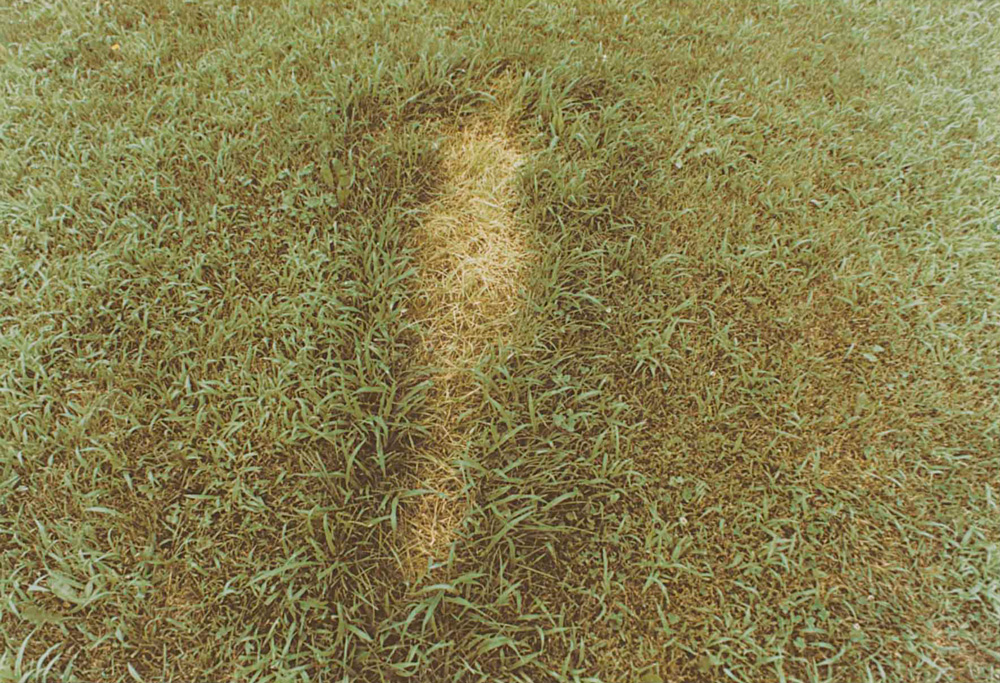

Human memory systems are subject to many imperfections, including memory distortions and the creation of false memories. Here, we demonstrate a case where memory distortion is adaptive, increasing the overall accuracy of memories. […]
Although participants’ memories were systematically distorted, they were distorted in a way that is consistent with minimizing their average error […]
Thus, memory distortion may not always be maladaptive: in some cases, distortion can result from a memory system that optimally combines information in the service of the broader goals of the person. Furthermore, this framework for thinking about memory distortion suggests that false memory can be thought of on a continuum with true memory: the greater uncertainty participants have about an individual item memory, the more they weight their gist memory [Gist traces are fuzzy representations of a past event]; with no item information, they weight only their gist memory.
{ PsyArXiv | Continue reading }
photo { Ana Mendieta, Untitled, from Silueta Series, Iowa, 1978 }
memory, photogs | August 20th, 2018 3:29 am
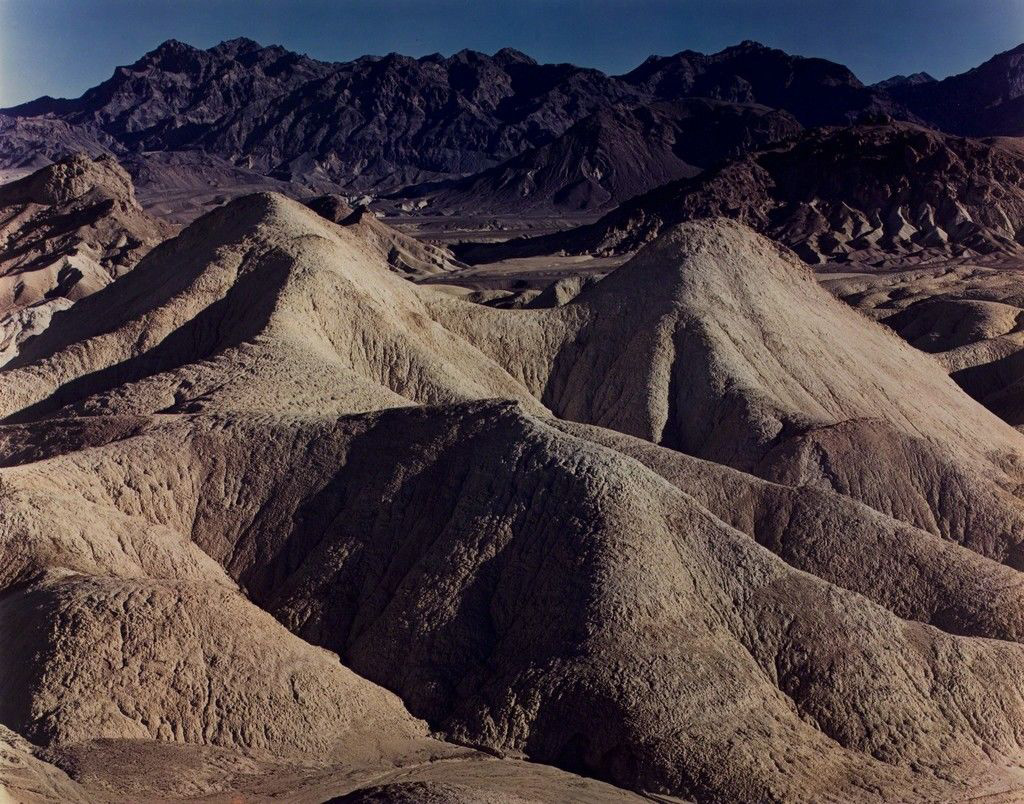

“Modern” Homo sapiens (that is, people who were roughly like we are now) first walked the Earth about 50,000 years ago. Since then, more than 108 billion members of our species have ever been born, according to estimates by Population Reference Bureau (PRB). Given the current global population of about 7.5 billion (based on our most recent estimate as of mid-2017), that means those of us currently alive represent about 7 percent of the total number of humans who have ever lived.
{ Population Reference Bureau | Continue reading }
photo { Edward Weston, Death Valley, 1947 }
flashback, photogs, pipeline, within the world | August 12th, 2018 3:27 pm
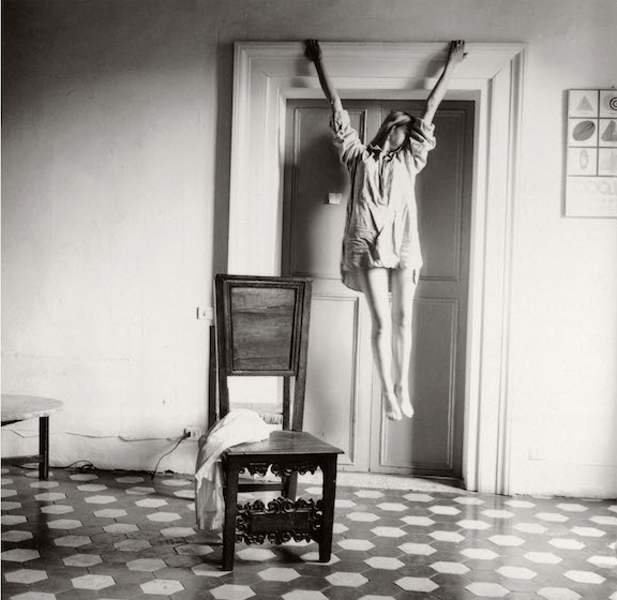

In 2014, stories appeared in national and international media claiming that the condition of “selfitis” (the obsessive taking of selfies) was to be classed as a mental disorder by the American Psychiatric Association and that the condition could be borderline, acute, or chronic. However, the stories were a hoax but this did not stop empirical research being carried out into the concept. The present study empirically explored the concept and collected data on the existence of selfitis with respect to the three alleged levels (borderline, acute, and chronic) and developed the Selfitis Behavior Scale (SBS).
{ International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction | Continue reading }
photo { Francesca Woodman, Untitled, Rome, Italy, 1977–1978 }
photogs, psychology | June 20th, 2018 8:13 am
photogs | February 12th, 2018 1:28 pm