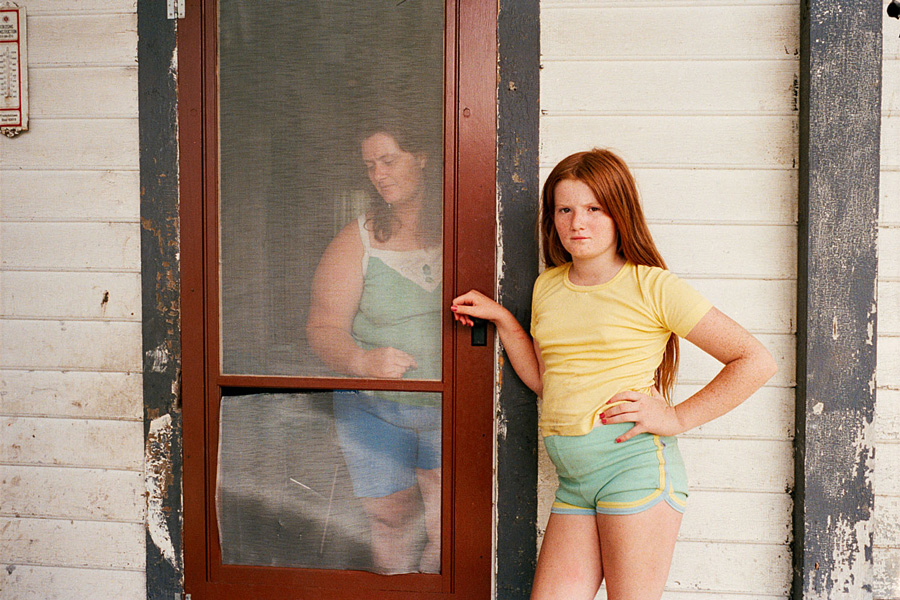economics
Apparently someone sat Elon Musk down and told him where Bitcoins come from […] The funny move here would be if Tesla Inc. had dumped all its Bitcoins at the highs. […] The source of value for Bitcoin is not its use as a currency or economic importance; the source of value for Bitcoin — for everything — is simple proximity to Elon Musk. […]
Mark Zuckerberg shared a picture of his pet goats on Monday, introducing them to the world as Bitcoin and Max.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
related { Tesla’s Musk halts use of bitcoin for car purchases }
buffoons, cryptocurrency | May 13th, 2021 1:26 pm
For a few minutes during trading on Wednesday, for example, the price of Ethereum Classic jumped well above $100 on the Coinbase exchange. The digital token was trading at less than $80 at other venues, offering an obvious opportunity for investors to make money simply by buying in one place and selling in another.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
cryptocurrency | May 11th, 2021 11:50 am
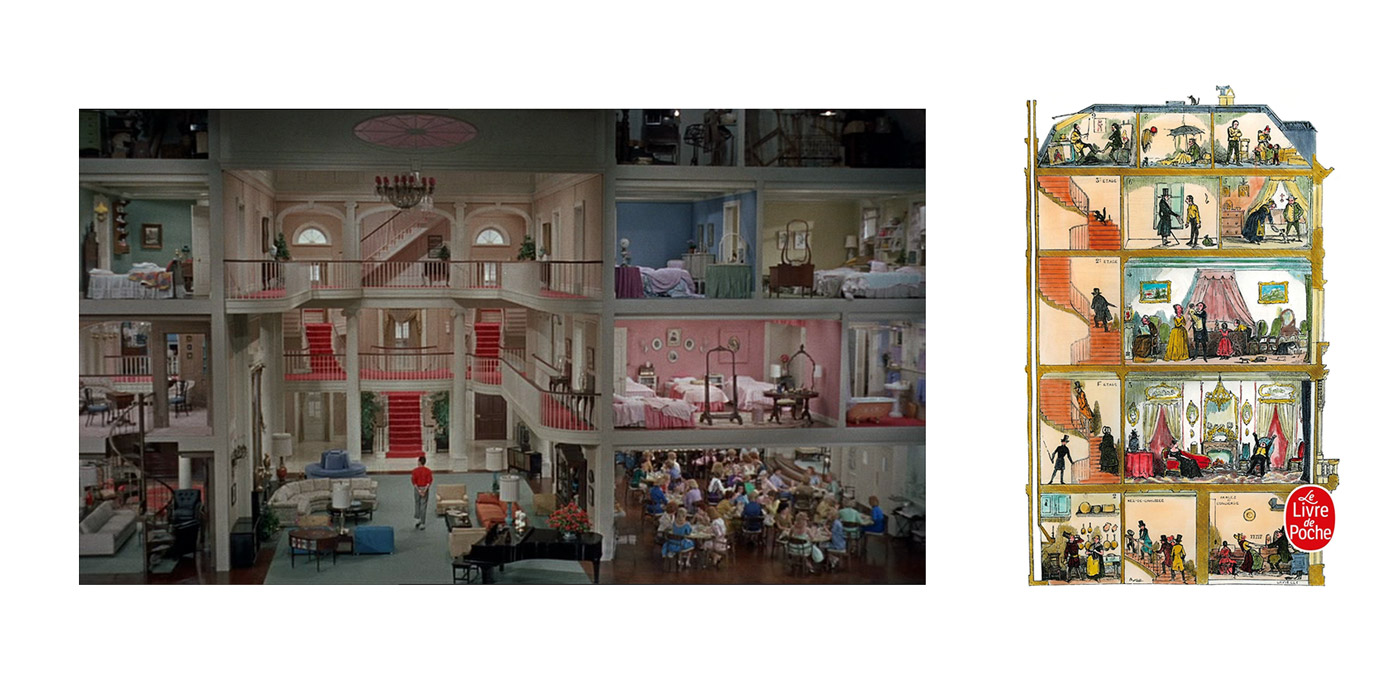

There are more real estate agents than actual houses for sale in the United States.
Any given day, you’re likely to see about half a million homes for sale, and there are 1.5 million members of the National Association of Realtors.
{ NPR | Continue reading }
images { Jerry Lewis, The Ladies Man, 1961 | Georges Perec, La vie mode d’emploi, 1978 }
halves-pairs, housing | May 4th, 2021 12:23 pm

if you want to build a global taxi service that people can hail from a smartphone app, one way to do it is to coordinate with the taxi commissions of hundreds of cities to get regulatory approvals and make sure that you comply with local requirements, and another way to do it is to completely ignore those regulations and just launch your app everywhere. The second approach might expose you to ruinous fines or shutdown orders or bad publicity or prison, but it also might work; you might end up so popular in so many places that the local regulators can’t ban you and will have to accept your proposed terms. […]
If you want to build self-driving cars, you will need to test them. […] [a] way to test them is to just send out a bunch of cars to drive themselves everywhere, without asking for permission, and see what happens. […]
Federal agencies say he’s breaking the rules and endangering people. Mr. Musk says they’re holding back progress. […] When asked to comment on the specifics of this article, Mr. Musk replied with a “poop” emoji.
{ Matt Levine/Bloomberg | Continue reading }
previously:
Driverify [cryptocurrency]: Developed by Tesla’s self-driving-car division. Cars mine Driverify with spare computing power while idling, and spend it bidding against each other for right-of-way if they arrive at a four-way stop sign at the same time (users can preprogram how aggressively their cars bid in these auctions). […]
Banned [by the SEC] because: in the Phoenix suburb where the system was being tested, a pedestrian and Driverify-equipped car reached an intersection at the same time. The car dutifully wired a bid, but the pedestrian failed to respond. The car interpreted this as a bid of zero and ran into her.
{ Astral Codex Ten | Continue reading }
related { NASA suspends SpaceX’s $2.9 billion moon lander contract after rivals protest }
buffoons, cryptocurrency, law, technology | May 2nd, 2021 6:51 am

The horses in these online races are NFTs, or “nonfungible tokens,” meaning they exist only as digital assets. […] But unlike the vast majority of NFTs each digital horse constitutes a “breathing NFT.” […] “It can breed, has a bloodline, has a life of its own. It races, it has genes it passes on, and it lives on an algorithm so no two horses are the same.” […]
One player sold a stable full of digital racehorses for $252,000. Another got $125,000 for a single racehorse. So far, more than 11,000 digital horses have been sold on the platform.
{ NY Times | Continue reading }
image { “Disaster girl” makes $500,000 in NFT sale of her viral meme }
cryptocurrency | May 1st, 2021 11:53 am

Patrick Mimran (born 1956 in Paris, France) is a contemporary French multimedia artist, composer, and the former owner and CEO of Lamborghini. […] In 1987 he sold Lamborghini to Chrysler and made, so it is said, «enough profit to be completely satisfied».
{ Wikipedia | Hamlet Hamster }
still { Con Artist (2009), a documentary about Mark Kostabi — not Patrick Mimran }
art, economics | April 21st, 2021 11:59 am
In 1997, David Bowie issued “bonds” that enabled their holders to earn a percentage of royalties from his back-catalog for the next ten years. An owner of a $1000 “Bowie Bond” would receive a 7.9% coupon each year. Prudential Insurance bought the first batch for $55 million.
At the outset, these securities seemed like a safe investment. Bowie’s songs were played regularly on the radio, and his albums were selling well, even decades after they were published.
Royalties from his work generated a steady income stream that was likely to continue. Bowie Bonds received a triple-A rating from Moodys, indicating they were as safe as U.S. government bonds.
But as online music sharing grew in popularity, Bowie’s album sales declined, and the bonds started to trade at a discount.
{ Dror Poleg | Continue reading }
also { Supervising cryptoassets for anti-money laundering | PDF }
economics, music | April 12th, 2021 7:25 am

My favorite line from this 9 page long paper (citing another study): “greater gender diversity in boards leads to excessive monitoring of executives.” P. 5.
Monitoring of executives is what boards are supposed to do. So the problem is that women directors do their jobs.
{ Richard W. Painter | Continue reading }
unrelated { “Females were less likely than males to approach a person in public to obtain drugs through cash and noncash transactions. […] Females were more likely than males to acquire drugs through sex.” | Gender Differences in Drug Market Activities | PDF }
economics, genders | April 2nd, 2021 12:18 am

Nomura and Credit Suisse are facing billions of dollars in losses after a U.S. hedge fund, named by sources as Archegos Capital, defaulted on margin calls. […]
A margin call is when a bank asks a client to put up more collateral if a trade partly funded with borrowed money has fallen sharply in value. If the client cannot afford to do that, the lender will sell the securities to try to recoup what it is owed.
Margin calls on Archegos Capital prompted a massive unwinding of leveraged equity bets. Shares in ViacomCBS and Discovery each tumbled around 27% on Friday, while U.S.-listed shares of China-based Baidu and Tencent Music plunged during the week, dropping as much as 33.5% and 48.5%, respectively, from Tuesday’s closing levels. […]
Morgan Stanley sold $4 billion worth of shares early on Friday, followed by another $4 billion in the afternoon. […] Goldman liquidated more than $10 billion worth of stocks in the block trades [and] sold $6.6 billion worth of shares of Baidu Inc, Tencent Music Entertainment Group and Vipshop Holdings Ltd, before the U.S. market opened on Friday […] Following this, Goldman sold $3.9 billion worth of shares inViacomCBS Inc, Discovery Inc, Farfetch Ltd, iQIYI Inc and GSX Techedu Inc […]
Hwang, who founded Archegos and ran Tiger Asia from 2001 to 2012, renamed it Archegos Capital and made it a family office.
{ Reuters | Continue reading }
Archegos borrowed a mere five times its capital. Closely regulated Goldman Sachs is at nearly seven times on a risk-weighted basis. […]
Hwang himself was a walking risk factor. He admitted to wire fraud in 2012 and in 2014 was banned from trading in Hong Kong for four years.
{ Reuters | Continue reading }
traders | March 29th, 2021 12:32 pm
Cannabis Delivery Services are illegal in Maine. Gifting Cannabis is illegal in Maine. Don’t worry though! It is still legal for an Adult age 21/+ to carry 2.5oz of Cannabis Flower and up to 5 grams of concentrates!
So under your scenario you are in Maine vacationing, living, etc… and you lost your weed. OH NO! Who do you call? The INCREDIBLES.ME Psychic Service! We have Psychics roaming all over Portland communicating with their deity, their spirit guides, and having religious moments of clarity. We can guarantee to find your LOST WEED!! (For a small, but very worth while fee!).
Just login to this site, and select the cannabis or cannabis products you lost, and give us your address. We will find YOUR weed and get it back to you ASAP. Fees vary based on the time it takes us to find your weed, the quantity of weed we have to locate, and the distance in which we have to travel to get YOUR LOST weed back to you.
{ Incredibles.me | Continue reading }
drugs, economics | March 28th, 2021 8:59 am
NYC man sells fart for $85, cashing in on NFT craze […] Ramírez-Mallis and his fellow farters compiled the recordings into a 52-minute “Master Collection” audio file. Now, the top bid for the file is currently $183. Individual fart recordings are also available for 0.05 Ethereum, or about $85 a pop.
{ NY Post | Continue reading }
unrelated { Illegal Content and the Blockchain }
cryptocurrency, haha, noise and signals, olfaction | March 19th, 2021 6:53 am

Under U.S. law, as soon as a work of art in any medium is created, the creator owns the copyright in that work. […] When we talk about “copyright”, we’re really talking about multiple rights (sometimes called a “basket of rights”). These include the right to control who makes copies of the original work […]
Typically, when someone buys a work of physical art, they are only purchasing the physical object. They are not purchasing the copyright in the work. […]
So if you own an original oil painting, you can display it in your home or wherever you want, and you can sell or loan the painting to someone, but you can’t make copies of it, sell prints, or make new works based on the original. […]
if you buy an NFT, my presumption is that you are only buying ownership in the NFT itself. You are not buying the copyright, unless there is a written contract […]
if I buy an NFT, and then I post it to Instagram with the message “Check out this cool NFT that I just bought!”, that’s creating many more digital copies. But this is true for all kinds of visual art these days, and the artist is free to go to Instagram and file a copyright takedown notice, requesting that the post be removed.
{ David Lizerbram & Associates | Continue reading }
image + header { The meme economy }
cryptocurrency, law | March 13th, 2021 10:33 am
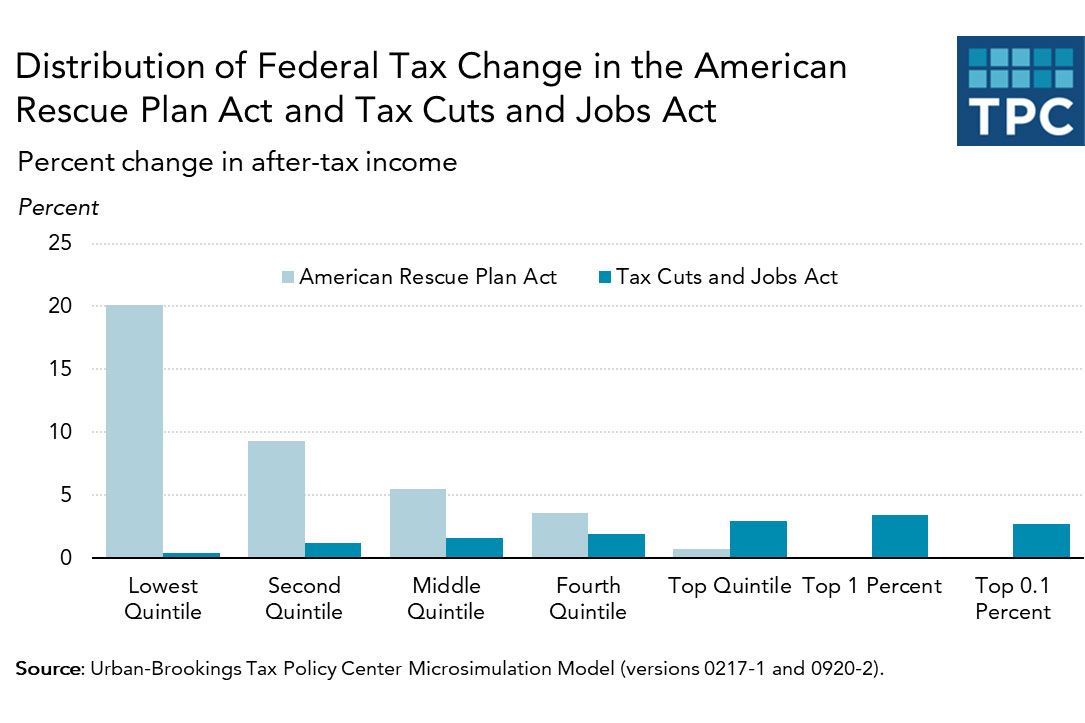
{ Trump and his party used their legislative majorities to redistribute income up the income ladder. Biden and his party are using theirs to distribute it down. | NY mag | full sotry }
U.S., economics | March 11th, 2021 10:57 am
Queen Elizabeth … a public servant, and an annual recipient of the taxpayer-funded sovereign grant — valued at $107.1 million (£82.2 million) in 2019…
{ CNN | Continue reading }
buffoons, economics | March 8th, 2021 7:31 am
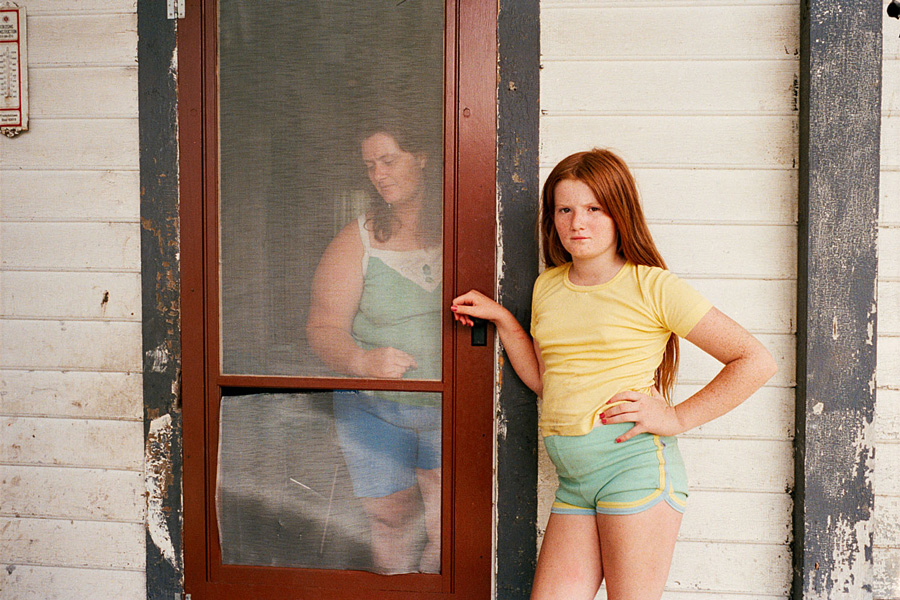
California Gov. Gavin Newsom on Friday revealed the most expensive budget in state history — a $227 billion spending plan highlighted by a $15 billion one-time surplus. How is it possible? […]
The Democratic governor and state lawmakers passed a budget last year with deep spending cuts to cover what they expected to be a $54.3 billion pandemic-induced shortfall. That estimate was wrong, as the recession was not as deep as they had anticipated […]
job losses have been concentrated among low-wage workers, who pay relatively little taxes […] wealthy residents have continued to make money and pay taxes, leading to much greater tax collections than officials predicted in early summer.
{ AP | Cal Matters }
photo { Sheron Rupp, Mansfiled, OH, 2001-2002 }
The World vs. SARS-CoV-2, economics, l.a. pros and cons | February 12th, 2021 7:49 am
haha, traders | January 28th, 2021 8:20 pm

What Trump needed to do to make Television City a reality was to bring together different stakeholders: locals (like the late actor Paul Newman) who wanted parks and a less imposing development, and Ed Koch [mayor of New York City]. […]
Koch said Trump was “squealing like a stuck pig.” Trump said Koch’s New York had become a “cesspool of corruption and incompetence.” Koch said Trump was a “piggy, piggy, piggy.”
Trump said the mayor had “no talent and only moderate intelligence” and should be impeached. […]
Trump promised that he would eventually build Television City “with or without the current administration” in City Hall. But he never did.
Although New York developer William Zeckendorf Jr. offered Trump $550 million for the site in 1989 — which would have given him a handsome return on the $115 million in borrowed money he used to acquire the Yards four years earlier — he refused to sell.
In 1994, with the Yards bleeding about $23.5 million in annual carrying costs, and long after Koch had departed City Hall, Trump’s bankers forced him to give up control of the site. The property went to a group of Hong Kong investors, including New World Development, for $82 million and the assumption of about $250 million in debt Trump had amassed.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
buffoons, economics, haha, new york | January 18th, 2021 9:37 am

California Water Futures Begin Trading Amid Fear of Scarcity
Water is joining gold, oil and other commodities traded on Wall Street […] Farmers, hedge funds and municipalities alike are now able to hedge against — or bet on — future water availability in California, the biggest U.S. agriculture market and world’s fifth-largest economy. […]
The futures are tied to the Nasdaq Veles California Water Index, which was started two years ago and measures the volume-weighted average price of water.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
economics, water | December 9th, 2020 11:42 am
So, your research argues that TV advertising is about 15 to 20 times less effective than the conventional wisdom says […]
There are, not surprisingly, objections to this research. Especially from the marketing industry. For instance, they’ll point to the brand-building aspect of advertising: “It’s not just about short-term sales,” they’ll say. Or the game-theory aspect — that is, if you don’t advertise your product and your rivals do, where does that leave you? […]
eBay believed that for every dollar they’re spending, they’re getting 50 cents of net profits. And what we showed is that on average, they’re losing more than 60 cents on every dollar. […]
Google actually did a fascinating study not too long ago, which concluded that close to 60 percent of ads on the internet are never, ever even seen.
{ Freakonomics | Continue reading }
economics, marketing | December 7th, 2020 11:23 am

U.S. government agencies from the military to law enforcement have been buying up mobile-phone data from the private sector to use in gathering intelligence, monitoring adversaries and apprehending criminals. Now, the U.S. Air Force is experimenting with the next step.
SignalFrame’s product can turn civilian smartphones into listening devices—also known as sniffers—that detect wireless signals from any device that happens to be nearby. The company, in its marketing materials, claims to be able to distinguish a Fitbit from a Tesla from a home-security device, recording when and where those devices appear in the physical world.
Using the SignalFrame technology, “one device can walk into a bar and see all other devices in that place,” said one person who heard a pitch for the SignalFrame product at a marketing industry event. […]
Data collection of this type works only on phones running the Android operating system made by Alphabet Inc.’s Google, according to Joel Reardon, a computer science professor at the University of Calgary. Apple Inc. doesn’t allow third parties to get similar access on its iPhone line.
{ Wall Street Journal | Continue reading }
photo { William Eggleston, Untitled (Greenwood, Mississippi), 2001 }
economics, spy & security, technology | November 28th, 2020 7:01 am