psychology

In this study, we examine whether perceived loneliness is greater among the Baby Boomers—individuals born 1948–1965—relative to those born 1920–1947, and whether older adults have become lonelier over the past decade (2005–2016). […]
Overall, loneliness decreases with age through the early 70s, after which it increases. We find no evidence that loneliness is substantially higher among the Baby Boomers or that it has increased over the past decade.
{ PsyArXiv | Continue reading }
quote { Going at the heart of social cognition: is there a role for interoception in self-other distinction? }
psychology, relationships | April 26th, 2019 9:30 am

Software from Amenity Analytics promises to automate this process by spotting when chief executive officers try to duck tough questions. The software, its makers say, can even pick up on the signs of potential deception that CIA and FBI interrogators look for—including stalling and the use of qualifiers—and can gauge the sentiment of what is said on calls and reported in public filings, issuing a positive or negative numeric score. The goal is to make it easier for investors to wade through information and quickly make trading decisions.
{ Bloomberg Businessweek | Continue reading }
previously { Former CIA Officer Will Teach You How to Spot a Lie }
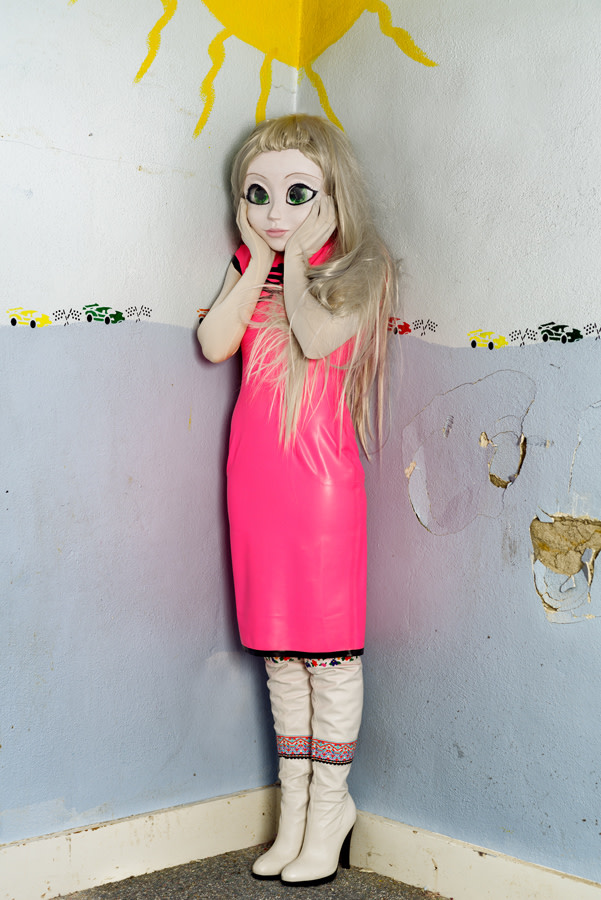
photo { Laurie Simmons, Blonde/Pink Dress/Standing Corner, 2014 }
psychology, technology, traders | April 22nd, 2019 6:58 am
Two alternative hypotheses have been proposed to explain why grunting in tennis may impede opponents’ predictions, referred to as the distraction account (i.e., grunts capture attentional resources necessary for anticipation) and the multisensory integration account (i.e., auditory information from the grunt systematically influences ball trajectory prediction typically assumed to rely on visual information). […]
our findings provide strong support for the multisensory integration account by demonstrating that grunt intensity systematically influences judgments of ball trajectory.
{ PLoS One | Continue reading }
noise and signals, psychology, sport | April 18th, 2019 12:50 pm

a team of psychology researchers began to challenge his ideas using a technique called “paradoxical thinking.” The premise is simple: Instead of presenting evidence that contradicts someone’s deeply held views, a psychologist agrees with the participant, then takes their views further, stretching their arguments to absurdity. This causes the participant to pause, reconsider, and reframe their own beliefs.
{ Quartz | Continue reading }
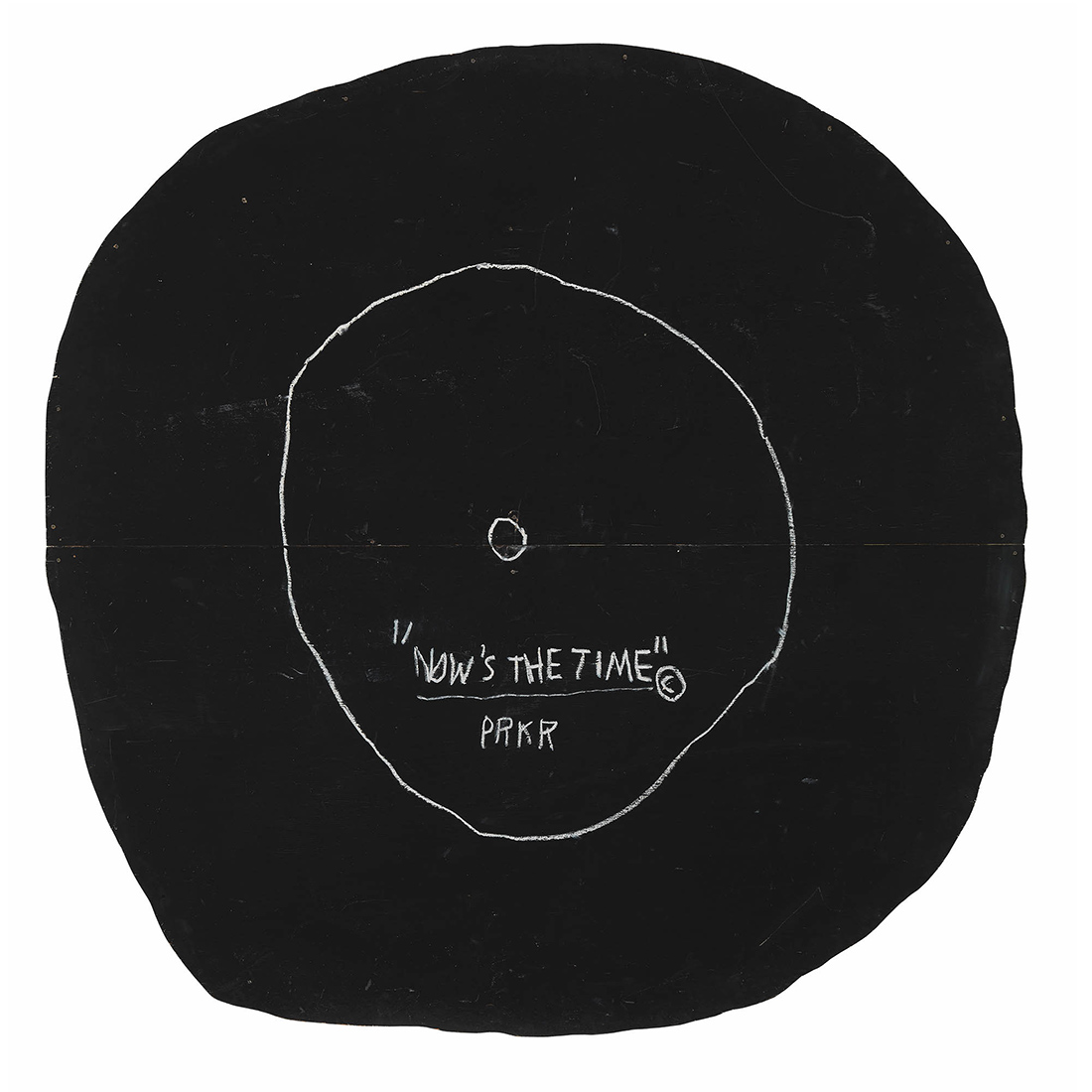
acrylic and oil stick on plywood { Jean-Michel Basquiat, Now’s the Time, 1985 }
psychology | April 13th, 2019 9:57 am

We have scientifically studied magic tricks to explore the human mind. For example, we use cutting-edge eye-tracking technologies to investigate how magicians misdirect our attention, and this work informs us about why people fail to see things right in front of their eyes. […] Magic works because we are typically unaware of our mind’s limitations, and most magic techniques rely on exploiting these surprising cognitive biases and limitations. Magicians don’t simply manipulate what you perceive – they manipulate your false beliefs about how much you can perceive.
{ The Psychologist | Continue reading }
related { we report a series of studies investigating the “paranormal potential” of magic performances }
eyes, psychology | March 27th, 2019 8:40 am

Paranoia is the most common symptom of psychosis, but paranoid concerns occur throughout the general population. […]
We suggest that paranoia should not solely be viewed as a pathological symptom of a mental disorder but also as a part of a normally-functioning human psychology.
{ Nature Human Behaviour | Continue reading | PDF }
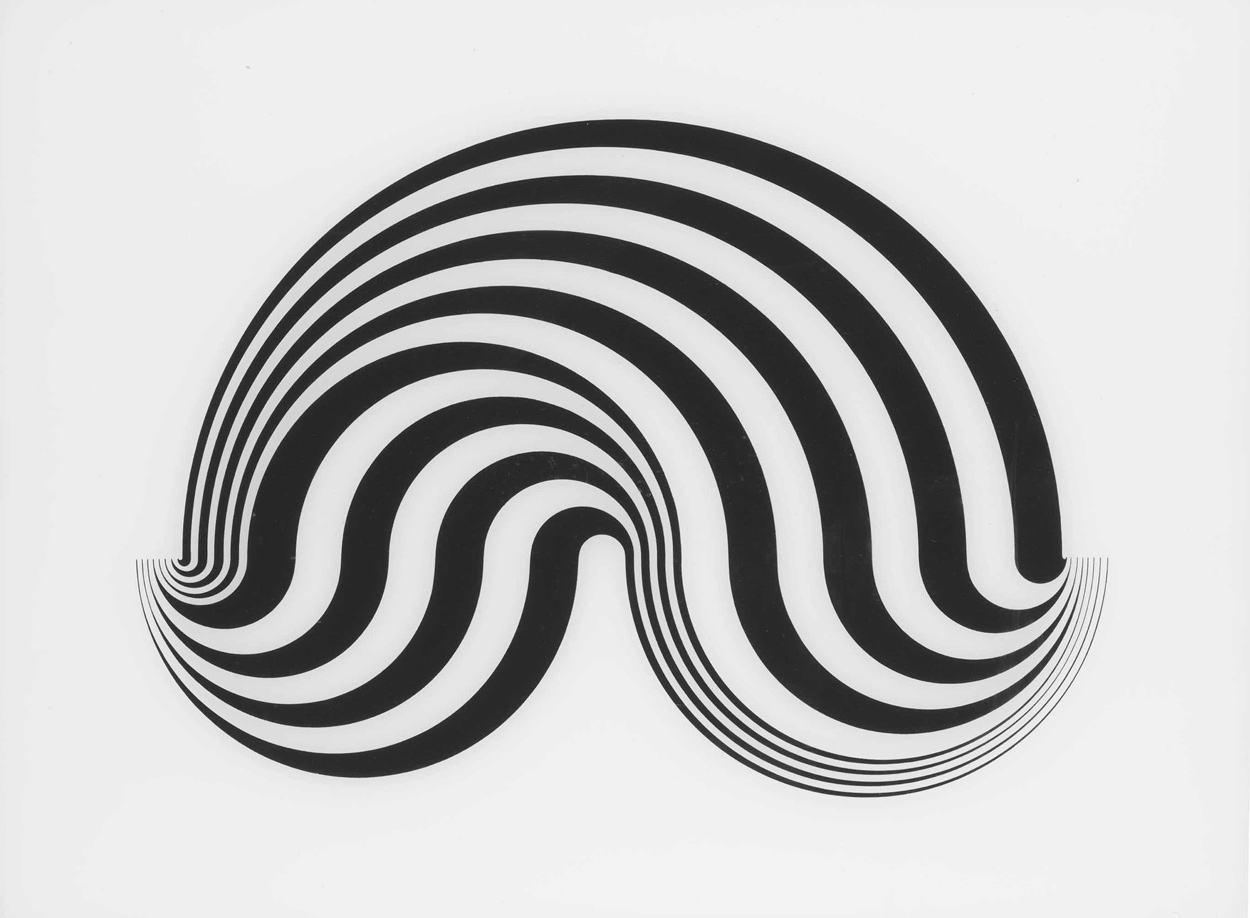
screenprint on Perspex { Bridget Riley, Untitled [Fragment 5/8], 1965 }
psychology, visual design | March 22nd, 2019 9:03 am
set of 10 woodcuts in ultramarine blue, on Okawara paper { Donald Judd, Untitled, 1988 }
psychology | March 12th, 2019 5:31 pm

The first cluster, or factor, of psychopathy is Fearless Dominance, which is characterized by social and physical boldness, adventurousness, and immunity to stress. The second factor of psychopathy is Self-Centered Impulsivity, which is is characterized by a narcissistic, callous and impulsive lifestyle and a willingness to take advantage of others without experiencing guilt. Note that those who score high in psychopathy tend to score high on both factors. In fact, if you just score high in Fearless Dominance, that might be an indication of a healthy personality! It’s the combination of these traits in a single package that makes it psychopathy. […]
In general, people did not find psychopathic characteristics particularly attractive for any form of relationship — whether it was a date, a short-term relationship, or a long-term relationship. […]
[T]hose with higher levels of psychopathic characteristics were more attracted to those with psychopathic characteristics. […] It wasn’t just psychopathy that predicted attraction to psychopathy. Many personality disorder features– such as histronic, narcissistic, obsessive-compulsive, schizotypal, passive-aggressive, self-defeating, antisocial, paranoid, borderline, avoidant, dependent, and sadistic features– were correlated with a preference for psychopathic characteristics.
{ Scientific American | Continue reading }
formica and industrial paint on wood { Lygia Clark, Planes in Modulated Surface 4, 1957 }
psychology | March 7th, 2019 2:23 pm

Contrary to the belief that happiness is hard to explain, or that it depends on having great wealth, researchers have identified the core factors in a happy life. The primary components are number of friends, closeness of friends, closeness of family, and relationships with co-workers and neighbors. Together these features explain about 70 percent of personal happiness.
{ Murray & Peacock, A model-free approach to the study of subjective well-being, 1996 }
related { Having Poor Quality Relationships Is Associated With Greater Distress Than Having Too Few }
photo { Janice Guy }
psychology, relationships | February 18th, 2019 10:12 am

Leveraging popular social networking sites, individuals undertake certain forms of behavior to attract as many likes and followers as they can. One platform that symbolizes people’s love for strategic self-presentation to the utmost degree is Instagram. […]
Narcissism is characterized by grandiose exhibition of one’s beauty and pursuit of others’ admiration. Posting selfies/groupies is associated with narcissism and need for popularity. […]
Instagram selfies and groupies symbolize social media users’ public display of narcissism. From an evolutionary psychological perspective on the renovated hierarchy of fundamental human motives and needs, this study examined the interaction effects of Instagram photo types (selfies, group selfies, long-shot photos taken by others, and neutral photos) and Instagram peer viewers’ individual difference factors (intrasexual competition [ISC] for mates, need for popularity [NfP], loneliness, and need to belong [NtB]) on intersexual attraction. […]
The findings confirmed the assumption that a potential mate who posts selfies and groupies is perceived by opposite-sex viewers to be more narcissistic compared to a potential mate who posts neutral photos.
{ Evolutionary Psychology | Continue reading }
photo { Thierry Mugler, Monster Show, Elle US, November 1991 }
psychology, relationships, social networks, weirdos | February 18th, 2019 10:00 am
Revising things makes people think they are better, absent objective improvement. We refer to this phenomenon as the revision bias. […]
We propose that the fact that revisions typically are intended to be improvements over their originals gives rise to an overgeneralized heuristic that revisions necessarily are improvements over their originals. Yet, as any author responding to editorial reviews knows, not every revision turns out better than before. […]
Things that are objectively unchanged (or even made worse) in the revision process may nonetheless be adopted, so long as observers believe they possess a “revised” version.
{ Harvard Business School | PDF }
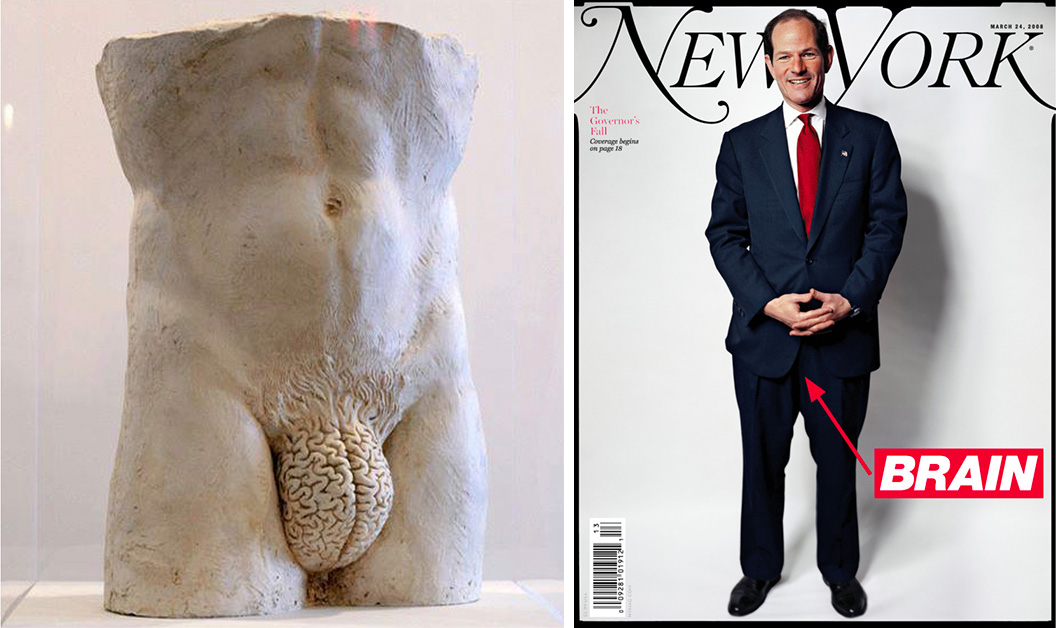
images { Sculpture by Yoan Capote | Barbara Kruger-annotated photo of Eliot Spitzer for New York magazine, 2008 }
halves-pairs, psychology | February 18th, 2019 9:33 am
If a rat sees another rat drowning, for example, it will forgo a chunk of chocolate to save its imperiled friend. […]
Scientists at the University of Chicago […] found that a white rat raised among only white rats will do nothing to save a black rat from a trap. Rats, like humans, can be biased in how they act on, or don’t act on, their empathy.
In a variant of the experiment, a white rat raised among only black rats would save a black rat from a trap — but would fail to save other white rats.
And a white rat raised among black and white rats rescued rats of both colors. The researchers found that it is not the rat’s color that determines which type of rat it will show empathy for, but the social context in which it was raised.
{ Henry James Garrett/NY Times | Continue reading }
related { when given a choice, do people avoid empathy? And if so, why? }
linocut on transfer paper { Christian Waller, The spirit of light, 1932 }
animals, psychology, relationships | February 12th, 2019 11:29 am

Advertising is ubiquitous in modern life. Yet might it be harmful to the happiness of nations? This paper blends longitudinal data on advertising with large-scale surveys on citizens’ well-being. The analysis uses information on approximately 1 million randomly sampled European citizens across 27 nations over 3 decades. We show that increases in national advertising expenditure are followed by significant declines in levels of life satisfaction.
{ University of Warwick | PDF }
photo { Joel Meyerowitz, New York City, 1968 }
marketing, psychology | January 18th, 2019 1:48 pm

if we asked our listeners […] what do you think you do on your face when you express anger? Everybody can give you something and it will be pretty much accurate. And the reason is because all of us have seen it. […] if you ask a blind person, “Hey, show me what you look like when you’re angry or when you’re sad,” you’ll get something that’s close but you don’t get the exact facial muscle movements that occur when those emotions occur spontaneously. However, when it occurs spontaneously, the exact facial muscle movements are exactly the same. So blind individuals produce them spontaneously but don’t produce exactly the same thing when you ask them to pose whereas sighted people do.
{ David Matsumoto/APA | Continue reading }
photo { Audrey Hepburn photographed by Richard Avedon on the set of Funny Face, 1956 | Richard Avedon was hired as visual consultant for Funny Face, directed by Stanley Donen. Shot partly in France, the film is loosely based on Avedon’s career as a fashion photographer in Paris. }
faces, psychology | January 15th, 2019 12:47 pm

We present a new tool that provides a means to measure the psychological and cultural distance between two societies and create a distance scale with any population as the point of comparison. Since psychological data is dominated by samples drawn from the United States or other WEIRD nations, this tool provides a “WEIRD scale.” […]
Decades of psychological research designed to uncover truths about human psychology may have instead uncovered truths about a thin slice of our species – those who live in Western Educated Industrialized Rich Democratic (WEIRD) nations. […]
Just how psychologically different are the nations of the world compared to each other and to the over-scrutinized United States? Many hard drives have been filled with the ways in which China and Japan differ from the United States and Canada, but just how psychologically distant is the culture of China from Japan, the United States from Canada, or Azerbaijan from Zambia? Here we introduce a robust method for quantifying this distance. […]
[We compared] the cultural differences between regions of the four largest populations—China, India, United States and European Union. These analyses reveal that the cultural differences between regions of the overscrutinized United States are considerably smaller than the European Union, China, or India. […]
The Far East has always held a certain exoticism, which may have driven a generation of cultural psychologists to document the many ways in which East Asian societies differ from the West. However, the most extensively researched East Asian nations aren’t anywhere near the extreme on the WEIRD scale and some are barely halfway. Moreover, there is considerable diversity within China, let alone between China, Japan, and Hong Kong. This diversity has been exploited by other researchers, for example, showing the role of agriculture on individualism and collectivism, but nowhere the levels performed within the United States, where we know state by state differences in psychological differences such as tightness-looseness. […]
Relatively little attention has been paid to the Middle East and Africa both by the World Values Survey and the psychological sciences. However, given the relative cultural distance to the United States and Africa’s large genetic, linguistic, and likely cultural variation, we have every reason to suspect the WEIRD scale will continue to stretch as we map out these psychological terra incognita. These regions, as well as other underrepresented regions, such as the South Pacific, may in fact hold a treasure trove of findings for the next wave of cultural psychologists.
{ SSRN | PDF }
psychology, within the world | December 2nd, 2018 1:36 pm

From 1936-1972, approximately 50,000 lobotomies were performed in the US. The majority of these occurred during the “lobotomy boom” which occurred in the late 1940s and early 1950s. Curiously, the lobotomy’s popularity coincided with a consensus within the medical community that it was ineffective. […]
Physician Walter Freeman performed approximately 10% of all US lobotomies during his medical career (El-Hai 2005). Although the procedure was widely used, it swiftly fell out of favor when the FDA approved the first antipsychotic drug in 1954. […]
In this paper, we propose the lobotomy’s popularity and longevity in the US was the result of the incentives generated by the institutional structure of mental health provision. Primarily, we note that funding for public mental hospitals and asylums were provided by state and federal governments on a very low per capita basis. This served to constrained revenues. Lobotomized patients were easier to manage (their brain damage often made them docile), and the procedure was comparatively cheaper than other treatment methods. These factors, in conjunction with little incentive to effectively treat patients provided by bureaucratic oversight, motivated physicians to perform cost and conflict minimizing treatment.
In contrast, physicians operating in private mental hospitals and asylums were funded by the patients, their caregivers, or through philanthropic donations. […] [L]obotomy was less used in private mental hospitals.
{ North Dakota State University Public Choice & Private Enterprise Research Paper Series | Continue reading }
acrylic, oil, oilstick and paper collage on three hinged wooden panels { Jean-Michel Basquiat, Self-Portrait, 1981 }
economics, health, psychology | November 28th, 2018 9:07 am

Previous studies have shown that male attractiveness can be enhanced by manipulation of status through, for example, the medium of costume. The present study experimentally manipulated status by seating the same target model (male and female matched for attractiveness) expressing identical facial expressions and posture in either a ‘high status’ (Silver Bentley Continental GT) or a ‘neutral status’ (Red Ford Fiesta ST) motor-car. […]
Results showed that the male target model was rated as significantly more attractive on a rating scale of 1–10 when presented to female participants in the high compared to the neutral status context. Males were not influenced by status manipulation, as there was no significant difference between attractiveness ratings for the female seated in the high compared to the neutral condition.
{ The British Psychological Society | PDF }
unrelated { Sweden plans to make sex toys safer because so many people get them stuck in their rectum }
motorpsycho, psychology, relationships, sex-oriented | October 29th, 2018 1:08 pm

Because more and more young people are constantly presented with the opportunity to access information and connect to others via their smartphones, they report to be in a state of permanent alertness. In the current study, we define such a state as smartphone vigilance, an awareness that one can always get connected to others in combination with a permanent readiness to respond to incoming smartphone notifications. We hypothesized that constantly resisting the urge to interact with their phones draws on response inhibition, and hence interferes with students’ ability to inhibit prepotent responses in a concurrent task. […]
Results show that the mere visibility of a smartphone is sufficient to experience vigilance and distraction, and that this is enhanced when students receive notifications. Curiously enough, these strong experiences were unrelated to stop-signal task performance. These findings raise new questions about when and how smartphones can impact performance.
{ PsyArXiv | Continue reading }
psychology, technology | October 18th, 2018 6:50 am
Procrastination is a familiar and widely discussed proclivity: postponing tasks that can be done earlier. Precrastination is a lesser known and explored tendency: completing tasks quickly just to get them done sooner.
Recent research suggests that precrastination may represent an important penchant that can be observed in both people and animals.
{ Learning & Behavior | Continue reading }
art { Vogue, June 1972 | Tom Wesselmann, Smoker #9, 1973 }
psychology, tom wesselmann | October 8th, 2018 7:16 am
In April 2018, the servers of the popular video game “Fortnite” crashed for 24 hr. During this period, Pornhub (a popular pornographic website) analyzed trends in pornography access, finding that: (a) the percentage of gamers accessing Pornhub increased by 10% and (b) the searches of pornographic videos using the key term “Fortnite” increased by 60%.
{ Journal of Behavioral Addictions | Continue reading }
related { How Fortnite became the most important video game on the planet }
update { Online divorce service says ‘Fortnite addiction’ cited in 200 divorces }
pochoir, brush and india ink { Roy Lichtenstein, Hand Loading Gun, 1961 }
leisure, porn, psychology, technology | September 17th, 2018 6:59 am





















