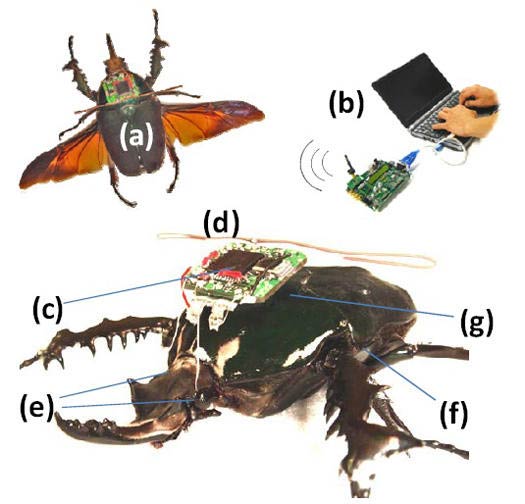
experts have identified two main categories of factors that make us more attractive to mosquitoes: biological aspects we can’t change and behaviors we can. […]
Dozens of diverse molecules distributed throughout your body come together to create your unique odor. […] it’s likely this distinctive mix of chemical compounds that draws mosquitoes in. It’s also possible that some people emit more of the odor that mosquitoes like […] mosquitoes are sensitive to different types of smells, even ones humans can’t detect, Dr. McBride said. For instance, “mosquitoes love forearm odor,” she said. “No one ever thinks of their arms as being smelly.” […]
Mosquitoes seem to gravitate toward people with Type O blood, he said, for reasons researchers haven’t confirmed. […]
The individual pattern of how you breathe — what Dr. Bazzoli called the “breathing signature” — also plays a role. Mosquitoes seek out carbon dioxide (which in part is why they’re so good at finding us), and the more we exhale, the more carbon dioxide we send into the air, inviting bugs our way. […]
Then there are the factors that are more dependent on how you act throughout the day. If you were to do a vigorous workout outside, you might breathe more heavily and exhale more carbon dioxide, which might usher in mosquitoes, Dr. Potter said. Sweat sends a powerful signal to mosquitoes too. […] And if you’ve had a few beach-side beers or happy hour margaritas, you might also emit some alcohol in your sweat, Dr. Bazzoli said, which can lure mosquitoes in. Alcohol might change the chemical makeup of your body odor, which could entice mosquitoes. […]
certain perfumes and scented soaps and lotions (including sunscreens) can attract mosquitoes […]
Certain clothing colors like black and dark blue can act like a mosquito magnet
{ NY Times | Continue reading }
health, insects | July 4th, 2023 12:02 pm
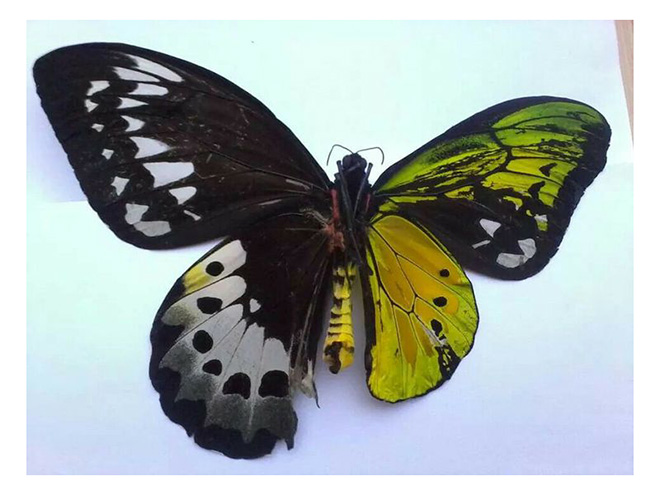

{ This butterfly is a bilateral gynandromorph: literally half male, half female | A gynandromorph is an organism that contains both male and female characteristics. The term gynandromorph, from Greek “gyne” female and “andro” male, is mainly used in the field of entomology. | Thanks Cassandra }
insects | May 24th, 2016 5:08 am
“Hasse” which was known in Ystad tavern circles, had a total of 146 wasp stings on the body including 54 on the genitals. He was so bloated that a neighbor thought it was a whale carcass lying on the lawn. […]
The autopsy and scene investigation revealed that “Hasse” tried to have sex with the wasp nest. They found semen on some of the dead wasps and a couple of “Hasse” pubic hair in the entrance of the nest. […]
Angry animal rights activists have reacted strongly to the event.
{ News Sweden | Continue reading | Thanks GG! }
incidents, insects | May 14th, 2013 2:55 pm

{ Since the early 1980s, artist Hubert Duprat has been utilizing insects to construct some of his “sculptures.” By removing caddis fly larvae from their natural habitat and providing them with precious materials, he prompts them to manufacture cases that resemble jewelers’ creations. | Leonardo | full story }
insects, visual design | February 22nd, 2013 1:26 pm

You walk into your shower and find a spider. You are not an arachnologist. You do, however, know that any one of the four following options is possible:
a. The spider is real and harmless.
b. The spider is real and venomous.
c. Your next-door neighbor, who dislikes your noisy dog, has turned her personal surveillance spider (purchased from “Drones ‘R Us” for $49.95) loose and is monitoring it on her iPhone from her seat at a sports bar downtown. The pictures of you, undressed, are now being relayed on several screens during the break of an NFL game, to the mirth of the entire neighborhood.
d. Your business competitor has sent his drone assassin spider, which he purchased from a bankrupt military contractor, to take you out. Upon spotting you with its sensors, and before you have any time to weigh your options, the spider shoots an infinitesimal needle into a vein in your left leg and takes a blood sample. As you beat a retreat out of the shower, your blood sample is being run on your competitor’s smartphone for a DNA match. The match is made against a DNA sample of you that is already on file at EVER.com (Everything about Everybody), an international DNA database (with access available for $179.99). Once the match is confirmed (a matter of seconds), the assassin spider outruns you with incredible speed into your bedroom, pausing only long enough to dart another needle, this time containing a lethal dose of a synthetically produced, undetectable poison, into your bloodstream. Your assassin, who is on a summer vacation in Provence, then withdraws his spider under the crack of your bedroom door and out of the house and presses its self-destruct button. No trace of the spider or the poison it carried will ever be found by law enforcement authorities.
This is the future. According to some uncertain estimates, insect-sized drones will become operational by 2030.
{ Gabriella Blum/Hoover Institution/Stanford University | PDF }
photo { Alexander Hammid, Maya Deren, 1945 }
future, insects, robots & ai, technology | August 19th, 2012 2:44 pm

Cockroaches are actually highly social creatures; they recognize members of their own families, with different generations of the same families living together.
Cockroaches do not like to be left alone, and suffer ill health when they are.
And they form closely bonded, egalitarian societies, based on social structures and rules. Communities of cockroaches are even capable of making collective decisions for the greater good.
By studying certain species of cockroach, we may even be able to learn some insights into how more advanced animal societies evolved, including our own.
{ BBC | Continue reading }
insects, science | May 3rd, 2012 12:37 pm

Multiple viral diseases are spread through vectors, like ticks and mosquitoes, that result in massive health care issues and epidemics worldwide – my question has always been, if the vectors are infected with the virus, are they getting a disease? And, what is in it for the organism? Or, what is driving the vector to spread the viral infection?
George Dimopoulous’ group at Johns Hopkins University shed light on these questions in their latest publication on Dengue virus and the effect on its main vector, mosquito species Aedes aegypti.
{ Smaller Questions | Continue reading }
health, insects, science | April 5th, 2012 12:10 pm

In the Cayman Islands, genetically modified mosquitoes are on the prowl. The insects are all male, and they’ve been engineered so that all their offspring die before reaching adulthood. By having sex with local females, they could father a new generation that perishes prematurely, before it gets the chance to spread diseases like dengue fever.
These GM insects, engineered by Luke Alphey at the University of Oxford, are part of a growing number of initiatives designed to fight disease by pitting mosquitoes against mosquitoes. Alphey’s tactic of breeding mosquitoes that beget unfit larvae is just one approach. Some groups are trying to make the insects more resistant to the disease-causing parasites they carry. Others have loaded them with life-shortening bacteria that outcompete those parasites. (…)
But all of these recent attempts to turn mosquitoes into malaria- and dengue-killing machines have something in common: The modified mosquitoes need to have lots of sex to spread their altered genes through the wild population. They must live long enough to become sexually active, and they have to compete successfully for mates with their wild peers. And that is a problem, because we still know surprisingly little about the behavior and ecology of mosquitoes, especially the males. How far do they travel? What separates the Casanovas from the sexual failures. What affects their odds of survival in the wild? How should you breed the growing mosquitoes to make them sexier?
{ Slate | Continue reading }
health, insects, science | January 19th, 2012 2:33 pm
The exchange of gifts at a wedding is customary in cultures all around the world. To my knowledge, however, there are no cultures in which bride and groom traditionally trade poisonous presents. (…)
If we were worried the bride might be brutally devoured on her way to the reception (by her new in-laws, perhaps), a gift of this kind might be precisely what she needs to stay alive.
An unlikely dilemma? For humans, perhaps so — but not for insects. And there are indeed certain species of insects whose mating rituals feature precisely this kind of gift, generally one given by the groom to the bride. His intentions in so doing are strictly honorable, of course, for females who receive such presents are better-equipped to deter predators.
{ Puff the Mutant Dragon | Continue reading }
insects, poison, science | December 19th, 2011 2:01 pm

Male seed beetles (Callosobruchus maculatus) have long spikes covering their penises [photo]. These spikes are thought to have evolved in response to female promiscuity, as a way of increasing the male’s chances of fertilizing a female’s eggs. Females, in response to the spikes, have evolved every man’s worst nightmare: spikes inside her vagina.
This is what evolutionary biologists call sexual conflict.
Males and females of a species have a common goal: to pass on their genes to the next generation. Sometimes, however, males and females have conflicting best strategies for getting that done. (…)
The penis of the male seed beetle punctures the female’s reproductive tract and, eventually, all those injuries will kill her. Females even have to kick the male constantly during mating to lessen the severity of the injuries–but she still won’t be deterred from hooking up again.
Why would male beetles want to harm females like this? (…)
While we’re on the topic of sharp penises that harm females, I thought I would throw in a little bed-bug action as well. Bed-bugs mate using what is known as “traumatic insemination.” Males bypass the female genitals entirely and pierce them in a specialized location on their bellies. They then ejaculate into the female sperm storage organ directly.
{ Molecular Love | Continue reading }
insects, science, sex-oriented, weirdos | August 3rd, 2011 10:32 pm

{ There are about 2,000 species of fireflies, a type of beetle that lights up its abdomen with a chemical reaction to attract a mate. That glow can be yellow, green or pale-red. In some places the firefly dance is synchronized, with the insects flashing in unison or in waves. The lightshow has also been beneficial to science—researchers have found that the chemical responsible for it, luciferase, is a useful marker in a variety of applications, including genetic engineering and forensics. | Smithsonian magazine | full article }
insects, science | July 1st, 2011 8:00 pm